Week 1#
Lecturer: Uma Maheswari, Faculty for BITS Pilani WILP
Date: 24/Jul/2021
Topics Covered#
- Intro to DBMS
- Advantages of DBMS
Operations of DBMS#
Database catalogue or dictionary is the metadata used by DBMS to save the information about the type of data, structures and constraints of the data.
Constructing the database is the process of storing the data on some stoprage and medium that is controlled by the DBMS
Manipulating a DB includes functions such as querying the DB to retrieve specidic data, updating the DB and querying the DB
Sharing the db regfers to sharing it via a server
access to DB
- Embedded SQL (EXEC block in C programming language)
- Create a special API to call SQL commands (JDBC, ODBC)
- Allow external code to be executed from within SQL
How to design database#
Three layer Architecture#
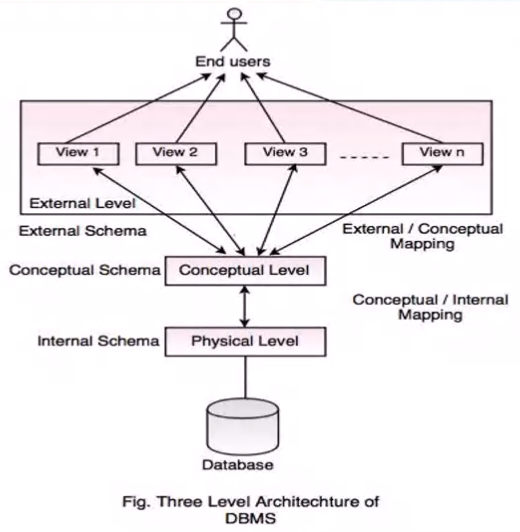
Each layer handles two issues
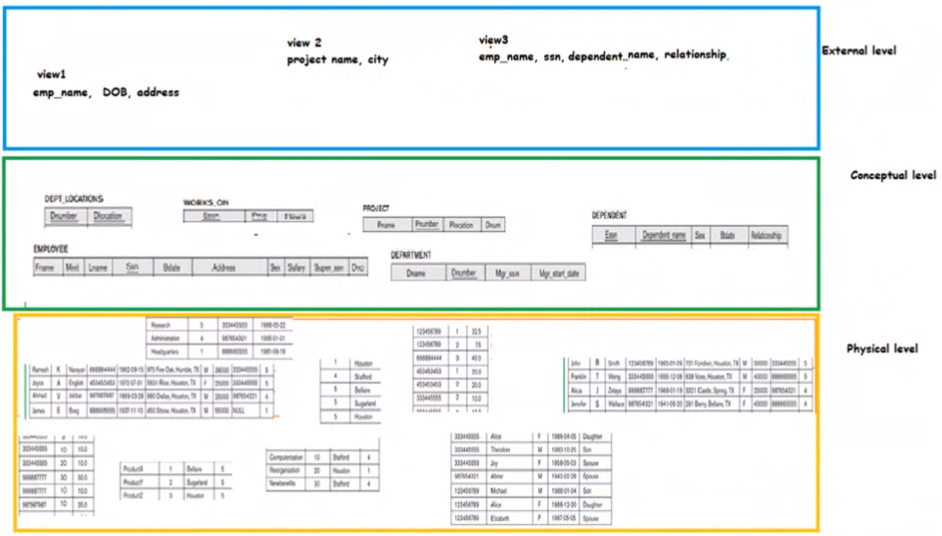
External Layer#
The above shows two views generated
Conceptual layer#
shows stored data in terms of the data model of the DBMS
Ina relational DBMS the conceptial schema descibes all relations that are stored in the DB
This couse is aimed at this level
Physical Layer:#
FM -> DM -> BM
All data is stored in the form of pages, and the file manager keeps track of these
The Disk manager brings it to memory
1. Specify additional storage details
2. File organization
3.
ETL (Extract Transform Load)#
Pysicall data independence#
irrespective of where the data is
Mapping#
Allow for external code to be executed from within SQL
EXECUTE can be used to run external scripts example python
protection
Sys protection (Against hw and sw)
sec protection (against unauth)
Characteristics of DB#
- self describing nature: there exists a data called meta data that describes the structure database. This is used by DBMS software and DB users who need infor about db structure
- Insulation between programs and data: There exists a data abstraction. The interface that allows for a program to access the data in the form of functions
- Support for multiple views: subsets of the database, contains vcirtual data derived from databse files but is not explicitly stored.
Multi User DBMS allow users to use distinct apps and must provide facilities to create multiple views - Sharing of data concurrency control software(make sure that multi user changes on data is controlled), Online transaction processing (OLTP) application
Transactions are rolled back since it is not commited
Example architecture#
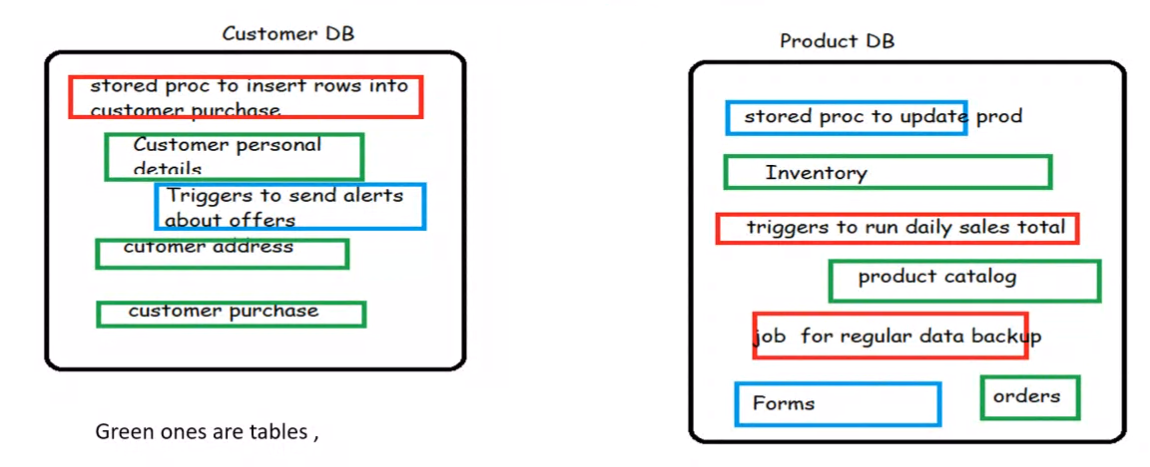
Data independence: all schemas are logical and the actual data is stored in bots in disk, so they both are inherently separate
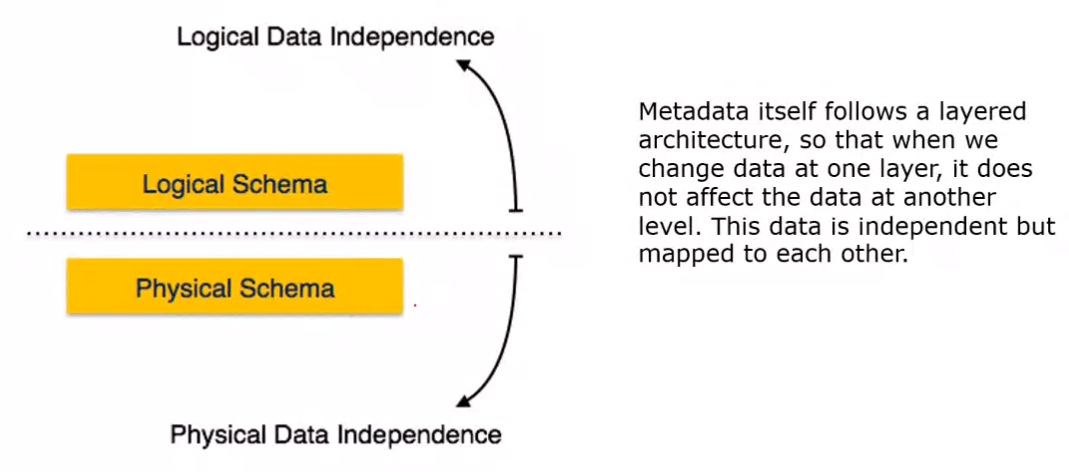
Mapping: The act of mapping two levels in a 3 level DBMS
System catalog#
It contains information such as:
- user accounts/default settings
- priveledges
- performance stats
- object sizing
- object growth
- table str
- index str
- table constraints
- user sessions
- internal db settings
- location of DB files
CRUD#
Create Read Update Delete
ERP and CRM#
History#