Week 6 (cont.)#
Lecturer: Pritam Bhattacharya, BITS Pilani, Goa Campus
Date: 5/Sep/2021
Topics Covered#
- Quick Sort
- Steps Done
- Algorithm
- Pivot Function
- Quick Sort Function
- Algorithm Analysis
- Space Complexity
- Time Complexity
Quick Sort#
Steps Done#
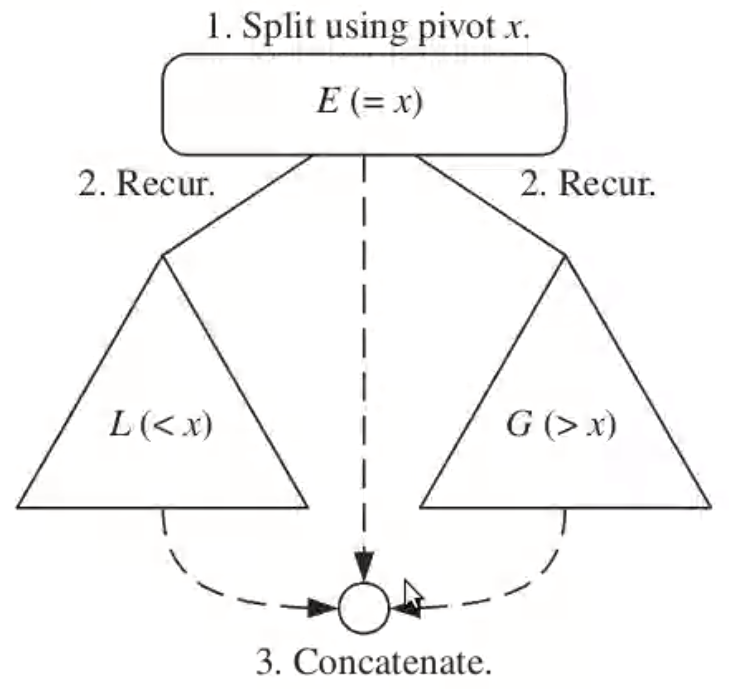
The actual sorting is done in a divide and conquer fashion denoted by the below steps:
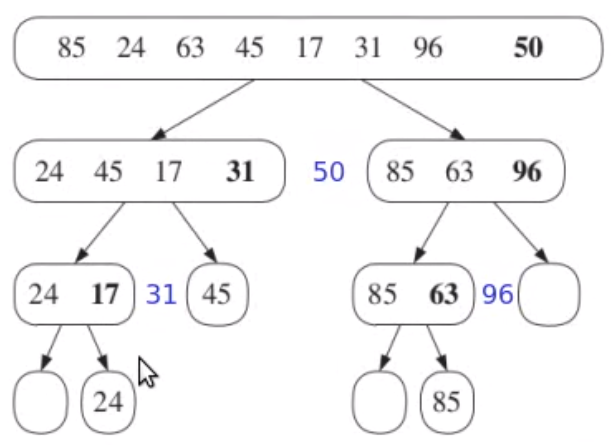
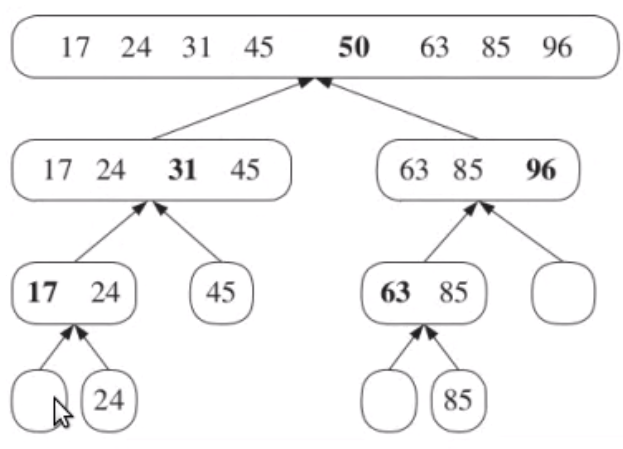
1. Divide: If \(S\) has zero or one element, return \(S\) immediately, it is already sorted, Otherwise pick a random element as a pivot element, and generate 3 parts:
1. \(L\) : The elements less than the pivot element
2. \(E\) : The element that is used as a pivot
3. \(G\) : The elements greater than the pivot element
2. Recur: Recursively sort the sequences \(L\) and \(G\)
3. Conquer: Concatenate the three sequences and return that
Algorithm#
Pivot Function#
partition(arr, low, high)
Input: An array of integers arr the lower index for the partition in the array and high the upper index
Ouput: pi, Partitioning index, the index where the pivot is placed
pivot = arr[high]
i = (low - 1)
for(j = low; j <= high - 1; j++) then
if arr[j] < pivot then
i++
arr[i] <-> arr[j]
arr[i + 1] <-> arr[high]
return (i + 1)

Quick Sort Function#
sort(arr, low, high)
Input: An array of integers arr the lower index for the partition in the array and high the upper index
Ouput: pi, Partitioning index, the index where the pivot is placed
if low < high then
pi = partition(arr, low, high)
sort(arr, low, pi - 1)
sort(arr, pi + 1, high)
Algorithm Analysis#
Space Complexity#
The in place algorithm does not take any extra space so we can say the space complexity is \(\mathcal{O}(1)\)
Time Complexity#
The partition function performs a single loop on the array elements, so the total number of operations done on a given level is proportional to n, so the time complexity here is \(\mathcal{O}(n)\).
In the best case, where the partition was balanced:
The sort function recursively calls sort by dividing the array into two segments and a pivot, so the size reduces at the rate of \(log\ n\) so the time complexity is \(\mathcal{O}(log\ n)\).
The total time complexity is: \(\mathcal{O}(n\ log\ n)\)
In the worst case, where the partition is not balanced
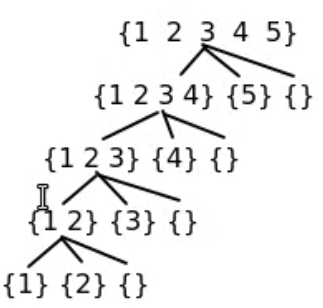
The sort function would end up creating \(n - 1\) levels, making the total time complexity as \(\mathcal{O}(n^2)\)
The reason why this sort is called Quick sort is because, the worst case happens very rarely and even if it does it can be fixed with a simple check to see if an array is already sorted.
