Week 10#
Lecturer: Barsha Mitra, BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Date: 30/Oct/2021
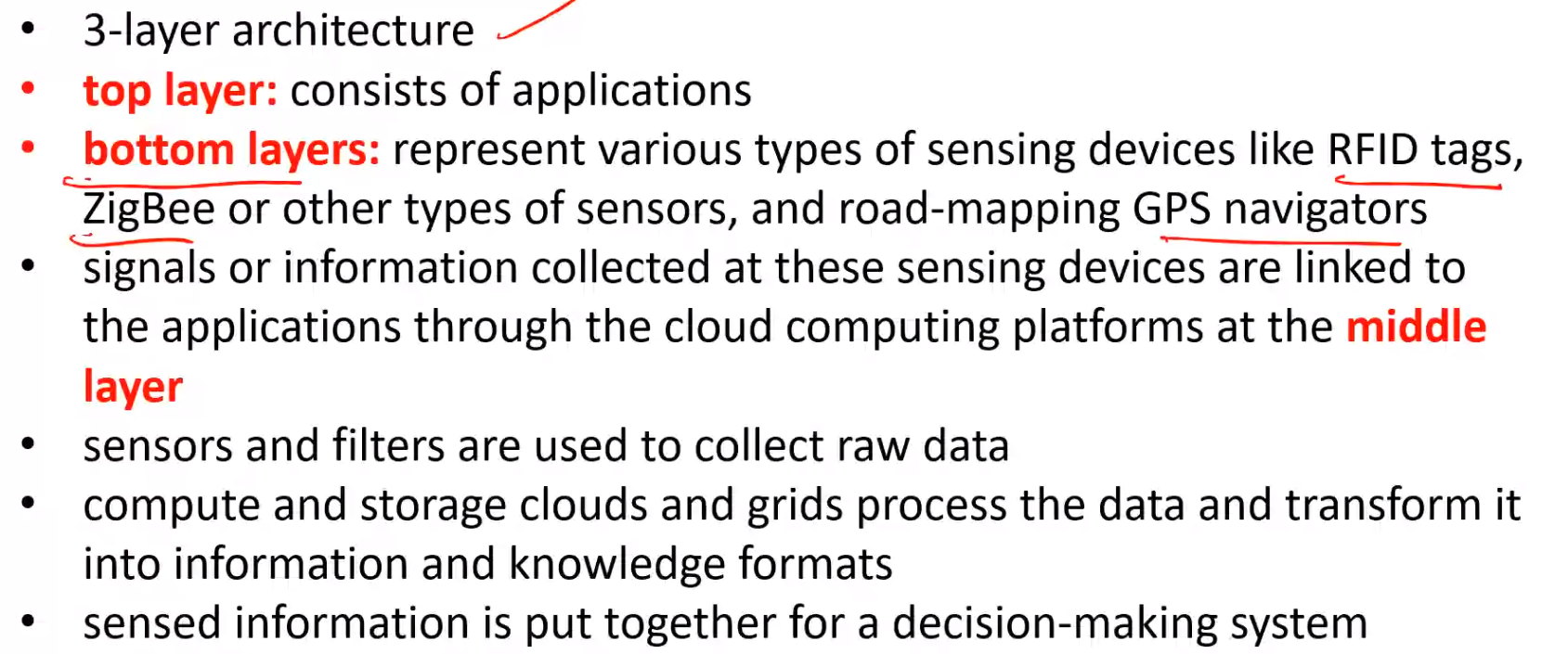
Scalable Lookup#
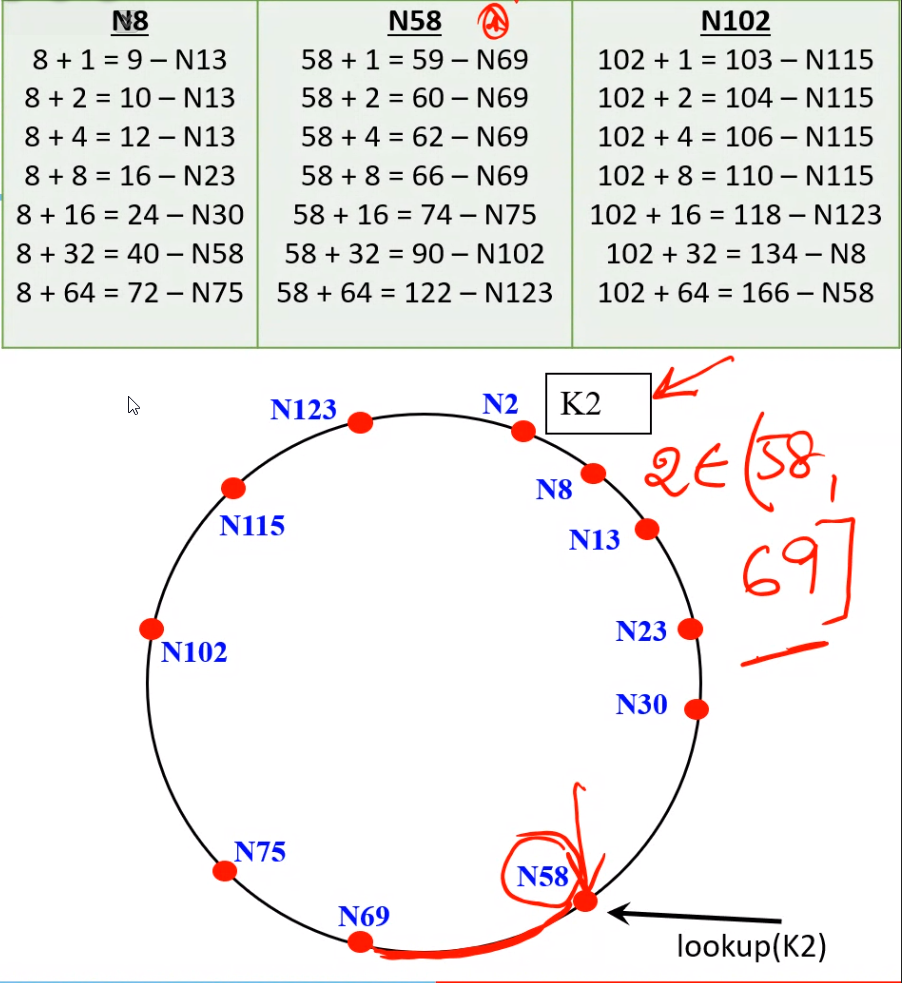
- Each node \(i\) maintains a routing table called finger table
- \(x^{th}\) entry \((1 \le x \le m)\) is the node identifier of the node \(succ(i + 2^{x - 1})\)
- Size of the finger table is bounded by \(m\) entries
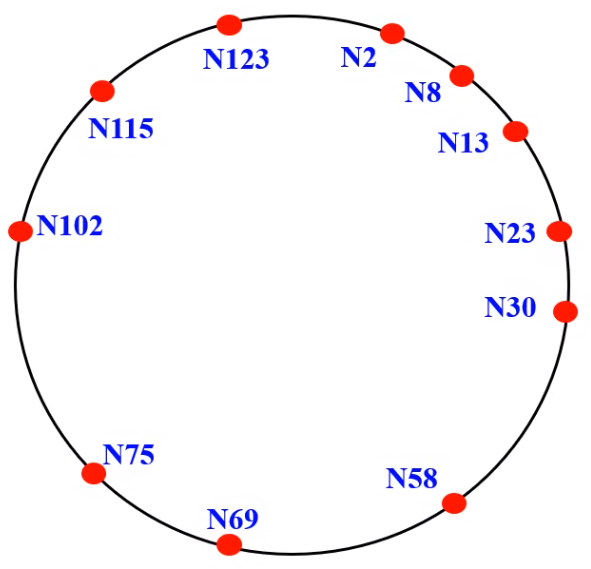
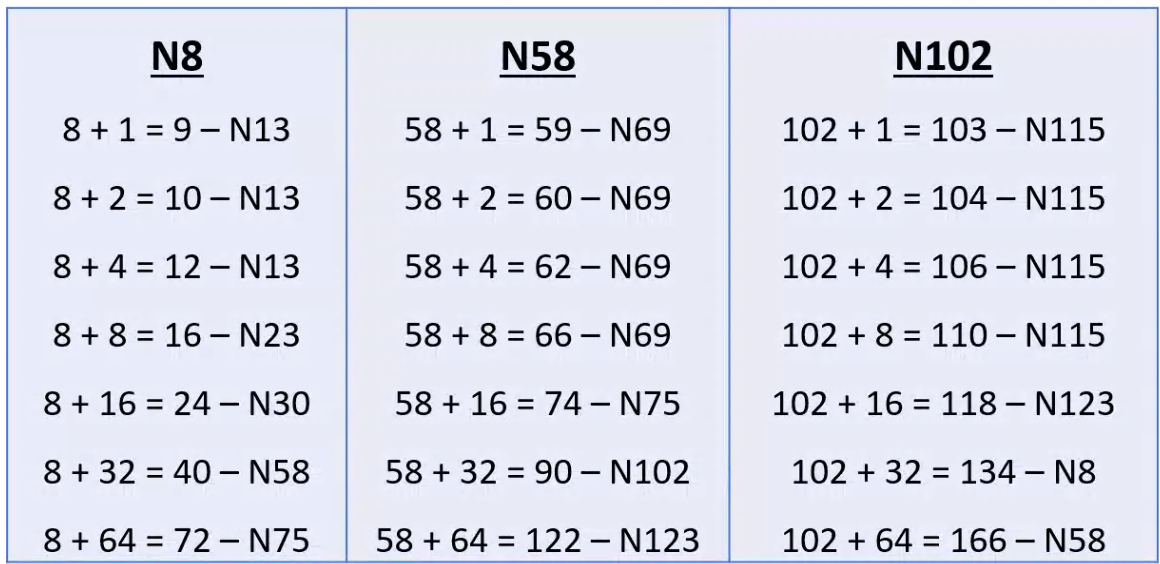
- Search is highly scalable
- For query on \(key\) at node \(i\), if key lies between \(i\) and its successor, then \(key\) would reside at the successor and the successors address is returned
- Else the finger table is searched
integer: successor <- initial value
integer: predecessor <- initial value
integer: finger [1...m]

Clustering for Massive Parallelism#
- Computer cluster
- Consists of a collection of interconnected stand-alone/complete computers
- Cooperatively work together as a single, integrated computing resource
- Explores parallelism job level
- Benefits of clusters
- Scalable performance
- HA
- fault tolerance
- Modular growth
- Use of commodity components
Design Objectives of Computer Clusters#
Packaging#
- Cluster nodes can be packaged in a compact or a slack fashion
- Compact CLuster:
- Nodes are closely packaged in one or more racks sitting in a room
- Nodes are not attached to peripherals
- Slack Cluster
- Nodes are attached to their usual peripherals
- May be located in different rooms, Different buildings, or even remote regions
Control#
- Cluster can be managed in a centralized or decentralized fashion
- Compact cluster normally has centralized control
- Slack cluster can be controlled either way
- Centralized Cluster:
- nodes are owned, managed and administered by a central operator
- Decentralized Cluster
- Nodes have individual owners
- Lacks a single point of control
Homogeneity#
- Homogenous cluster
- Uses nodes from the same platform/architecture etc
- Heterogenous Cluster
- Uses nodes of different platforms
- Interoperability is an important issue
Fundemental Cluster Design Issues#
- Cluster ob Management
- Achieve high system utilization
- Job management software is required to provide batching, load balancing, parallel processing, and other functionality
- Single System Image
- Cluster is a single system
- Appealing goal, very difficult to achieve
- SSI techniques are aimed at achieving this goal
- Avail;ability Support
- Redundancy in processors, memory, disks, IO devices, networks and operating system images
- Fault tolerance and recovery
- Eliminate all single point of failure
- Tolerate faulty conditions up to a certain extent through redundancy
- Critical jobs running on the failing nodes can be saved by failing over to the surviving node machines
- Rollback recovery schemes for periodic checkpointing
Single System Image#
- Motivation - Allows a cluster toi be used, controlled and maintained as a familiar workstation
- Features:
- Single system
- single control
- symmetry
- location transparent
- single ob management system
- single user interface
- single process space
HA (High Availability)#

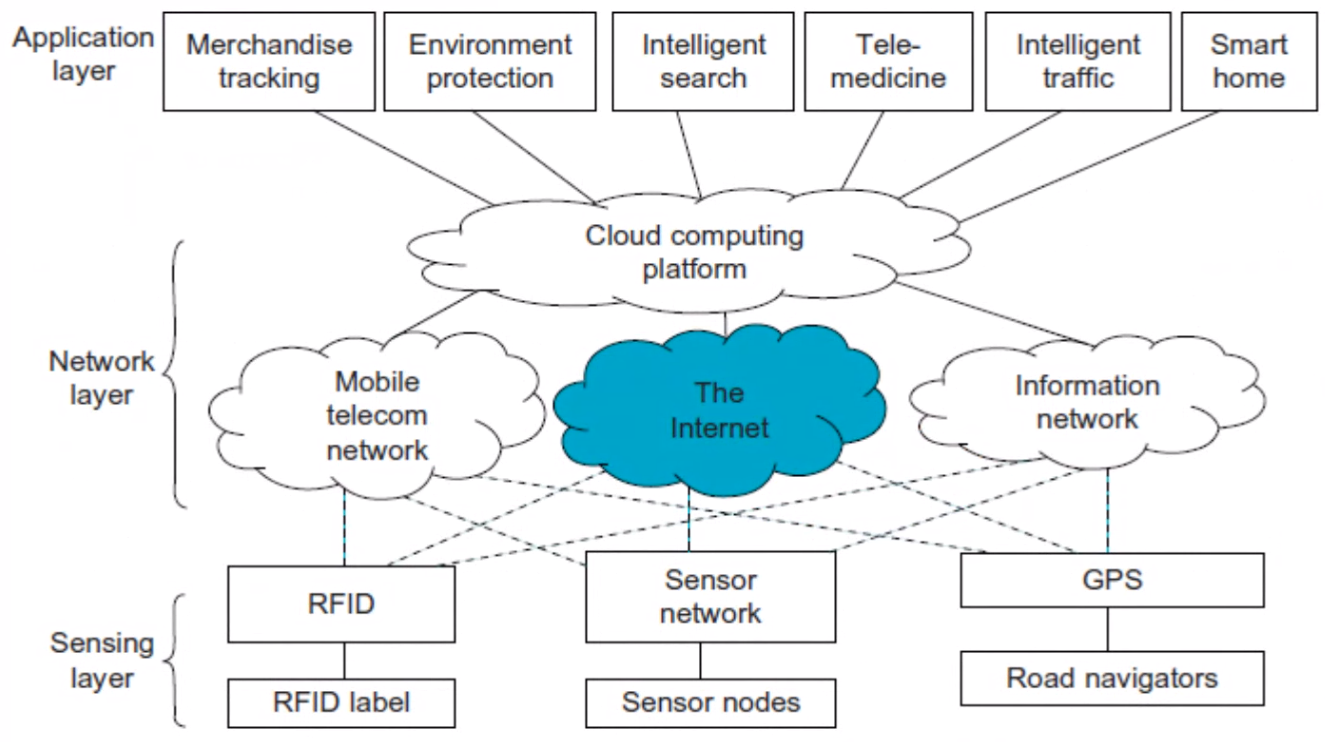
IoT for Ubiquitous Computing#

Architecture of IoT#