Week 6 (cont.)#
Lecturer: G Venkiteswaran, Faculty for BITS Pilani
Date: 7/Sep/2021
Topics Covered#
Special Matrices#

Similarity Of Matrices#
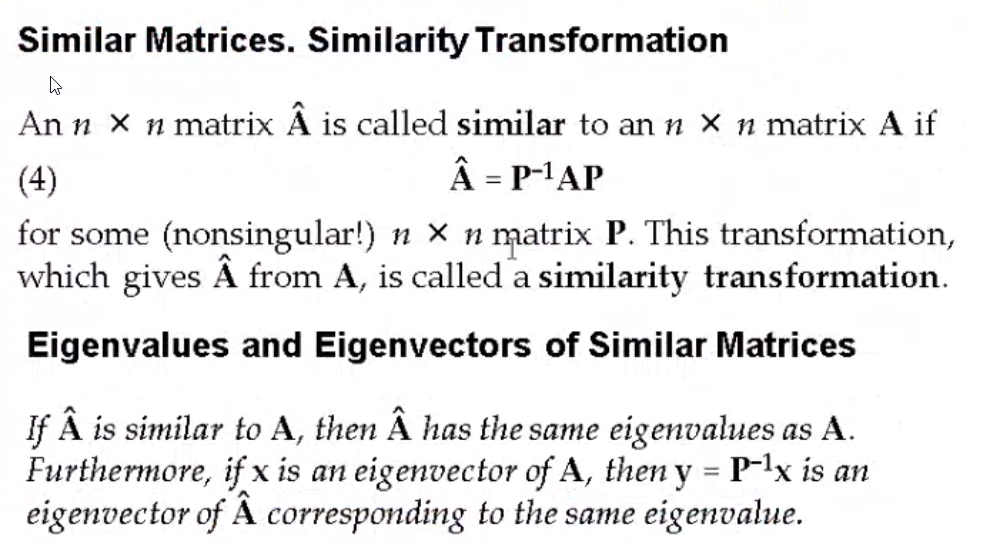
>> A = rand(4, 4)
A =
5.8181e-01 9.6943e-01 4.2533e-01 6.4573e-01
5.4844e-01 3.2016e-01 9.8479e-01 7.1938e-02
9.0286e-01 8.2269e-01 6.9796e-02 2.7225e-01
3.1388e-01 6.8389e-03 1.9440e-01 5.5537e-01
>> eig(A)
ans =
2.0028 + 0i
-0.5037 + 0.2040i
-0.5037 - 0.2040i
0.5318 + 0i
>> P = [6, 10, 11, 2; 2, 3, 5, 6; 19. 21. 61, 63; 39, 37, 79, 83]
P =
6 10 11 2
2 3 5 6
19 21 61 63
39 37 79 83
>> det(P)
ans = 1.1352e+04
>> B = inv(P) * A * P
B =
-13.8730 -16.5433 -39.9569 -38.2545
19.8346 23.1043 56.8459 55.2196
-7.9618 -9.4378 -25.1538 -24.5634
5.5832 6.7917 18.0890 17.4496
>> eig(B)
ans =
2.0028 + 0i
0.5318 + 0i
-0.5037 + 0.2040i
-0.5037 - 0.2040i
We see that \(A\) and \(B\) both share the same Eigen values, so \(A\) and \(B\) are similar matrices
So for a random matrix \(P\), we can find a similar matrix for \(A\) by doing:
\(B = P^{-1} . A . P\)
Diagonalization#
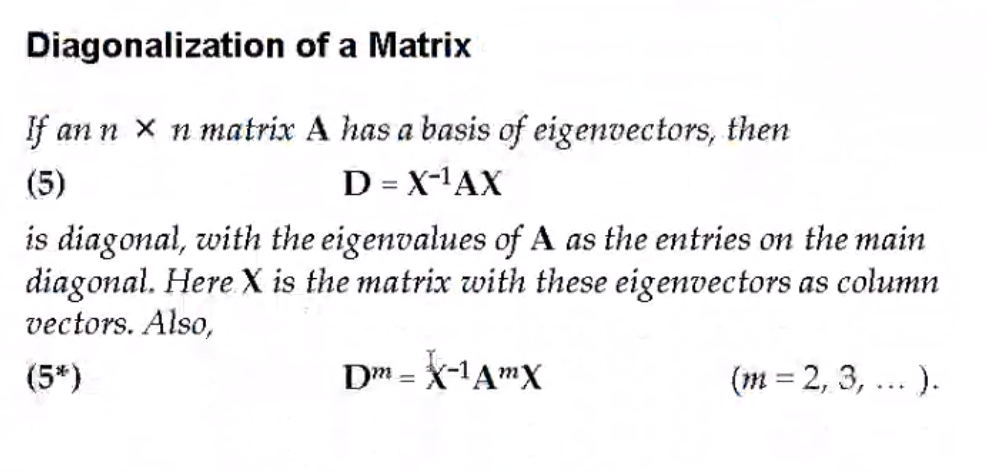

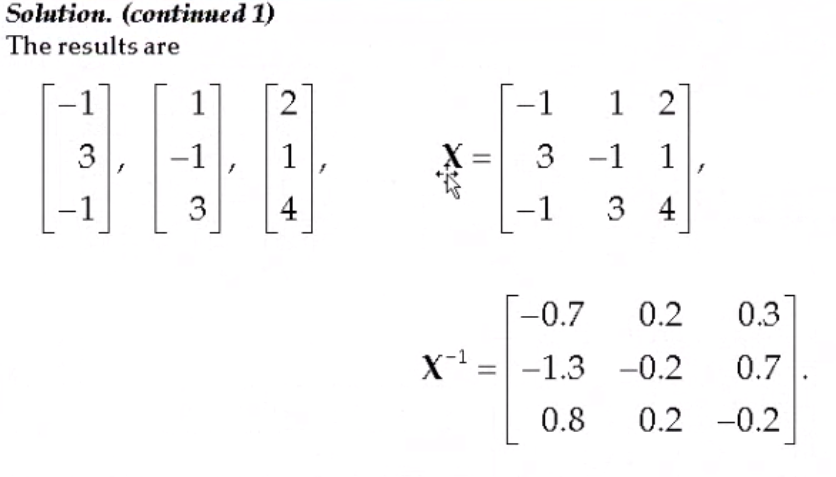
These 3 vectors are independent so,

Dominant Eigen Value#

Rayleigh's Quotient#

Go through the excel sheet
Power Method for#






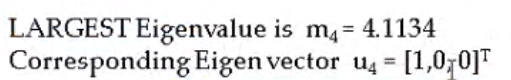
Convergence of Power Method#



