Week 11#
Lecturer: Pritam Bhattacharya, BITS Pilani, Goa Campus
Date: 30/Oct/2021
Linked List#
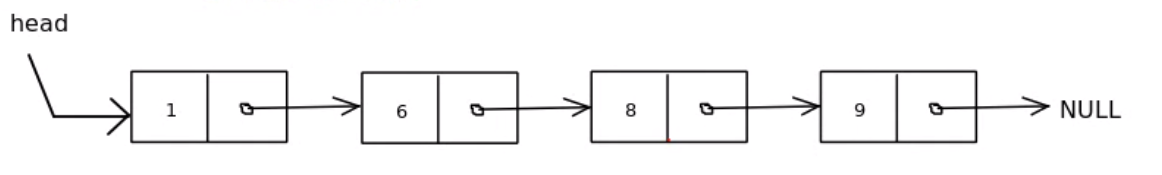
The linked list has a node where the node has a data and a pointer component that points to the next node (can be a node or null if it ends in this node)
struct Node {
int data
struct Node* next
}
ADT Operations#
first()-> This function returns the head of the linked list
first() { return head; }last()-> This function returns the last element of the linked list
last() { if(head == NULL) { return NULL } struct Node* temp = head while(temp -> next != NULL) { temp = temp -> next } return temp }before(p)-> This function returns the previous node to a given node p
before(struct Node* p) { if(p == head || p == NULL) { return NULL } struct Node* curr = head while(curr -> next != p) { curr = curr -> next } return curr }after(p)-> This function returns the next node
after(struct Node * p) { if(p == NULL) { return NULL } return p -> next }insertBefore(p, key)-> Insert a node before p with the key value
insertBefore(struct Node* p, int key) { if(head == NULL || p == NULL) { return ERROR } struct Node* newNode; newNode -> data = key newNode -> next = pos struct node* curr = head while(curr -> next != p && curr -> next != NULL) { curr = curr -> next } if(curr -> next == NULL) { return ERROR } curr -> next = newNode }insertAfter(p, key)-> Insert a node with value key to a position after p
insertAfter(struct Node* p, int key) { if(p == NULL) { return ERROR } struct Node* newNode newNode -> data = key newNode -> next = p -> next p -> next = newNode }remove(p)-> remove the node from the linked list
remove(struct Node* p){ if(p == NULL || head == NULL) { return NULL } struct Node* curr = head while(curr -> next != p && curr -> next != NULL) { curr = curr -> next } if(curr -> next == NULL) { return NULL } curr -> next = p -> next return p }
Double Linked list#
In a doubly linked list the Node contains the next node as well as the previous node as well along with the data. The struct would look somthing like this:
struct Node {
int data
struct Node* next
struct Node* prev
}
The ADT functions can now utilize the previous pointer for reference in operations such as insert before and insert after and one must also make sure to correctly set the previous and next pointers as well.
