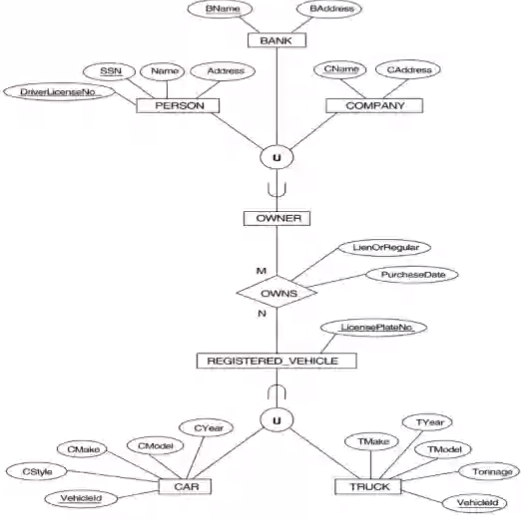
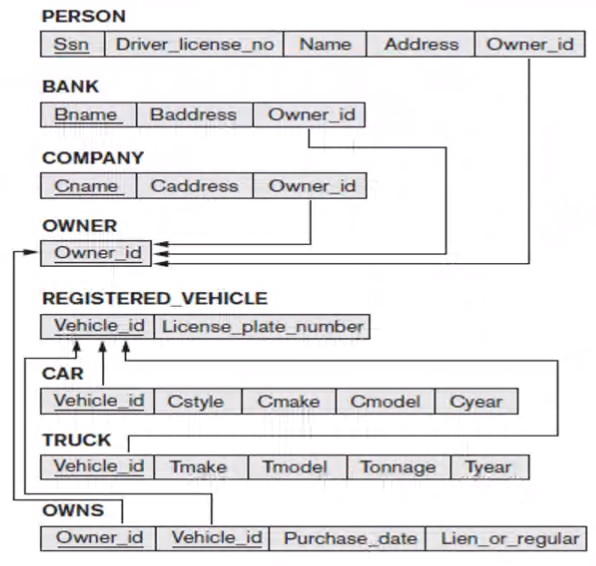
Week 6#
Lecturer: Uma Maheswari, Faculty for BITS Pilani WILP
Date: 21/Aug/2021
Topics Covered#
- Logical Design Phase
Logical Design Phase#
A summary of design phases:
Converting strong entity types:#
- Each entity type becomes a table
- single valued attributes becomes a column
- Derived attributes are ignored
- Composite attributes are represented by components
- Multivalued attributes are represented by a separate table
- The key attributes of the entry type becomes the primary key of the table
Entity Example 1#
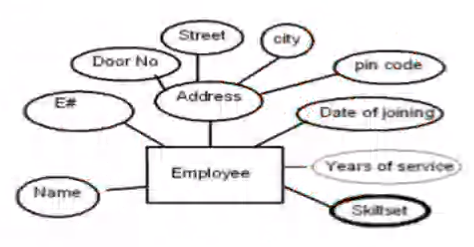
- Here address is a composite attribute
- Years of service is a derived attribute so can be ignored
- Skill set is a multivalued attribute
The converted relational schema for the above example:
Employee (E#, Name, Door_No, Street, City, Pincode, Date_Of_Joining)
Emp_Skillset(E#, Skillset)
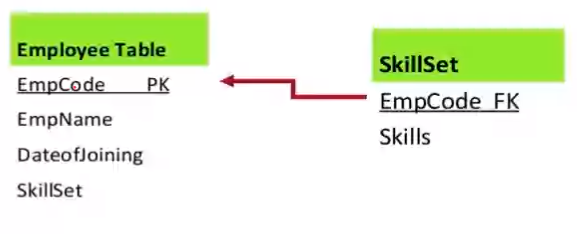
Entity Example 2#
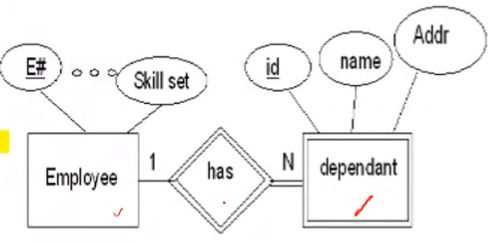
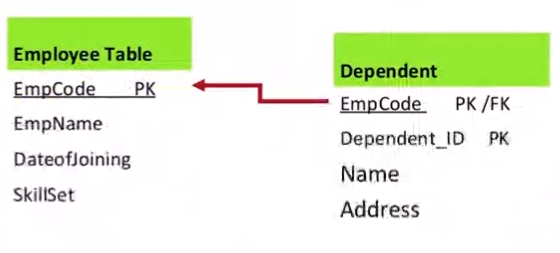
- Weak entity types are converted into a table oif their own, with the primary key of the strong entity acting as a foreign key in the table
- This foreign key along with the key of the weak entity form the composite primary key of this table
The converted relational schema for the above example:
Employee (E#, ...)
Dependant(E#, Dependant_ID, Name, Address)
Converting relationships:#
Binary 1:1#
Case 1: Combination of participation types#
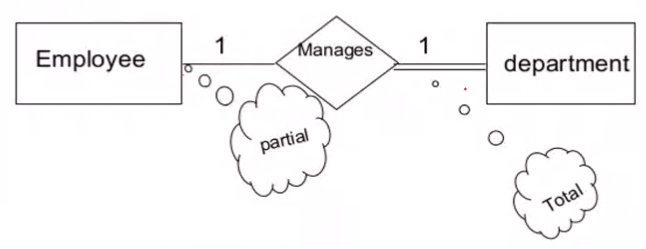
- The primary key of the partial participant will become the foreign key of the total participant
- The manager employee for the department will be a foreign key wrt Employee table
The converted relational schema:
Employee(E#, Name, ....)
Department(Dept#, Name, .... , MgrE#)
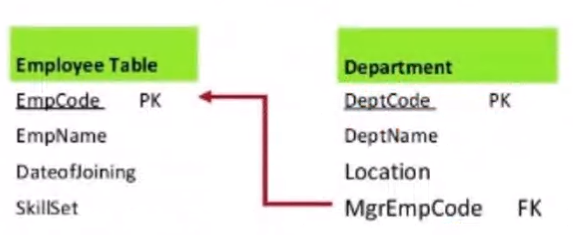
Case 2: Uniform participation types#

The converted relational schema:
Employee(E#, Name, ....)
Chair(Item#, Model, Location, used_by)
Employee(E#, Name, .... , Sits_on)
Chair(Item#, Model, Location)
Binary 1:N#
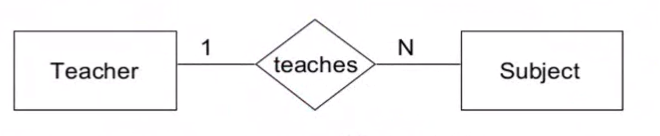
- Teacher in Subject table is the foreign key for Teacher entity
The converted relational schema:
Teacher(ID, Name, Telephone, ....)
Subject(Code, Name, .... , Teacher)
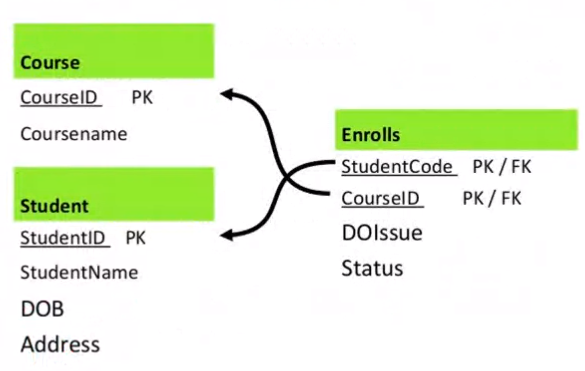
Binary M:N#
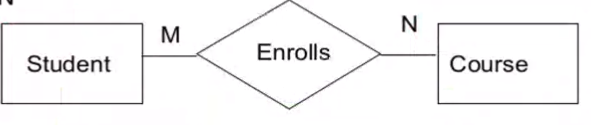
- The relation is moved to a separate table
- This table uses the PK of the other two tables as the foreign keys
The converted relational schema:
Student(Sid#, Title, .... )
Enrolls(Sid#, C#)
Course(C#, CName, .... )
Self Referencing Binary 1:1#
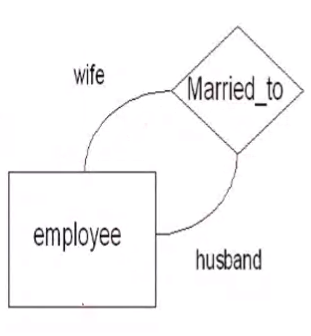
- E# is the primary key
- Spouse is the foreign key to employee table
The converted relational schema:
Employee(E#, Name, .... , Spouse)
Self Referencing Binary 1:N#
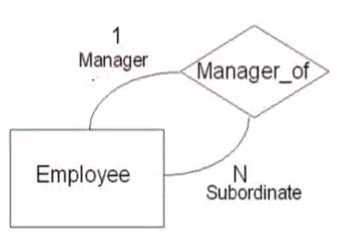
- Manager is the FK to the table Employee
The converted relational schema:
Employee(E#, Name, .... , Manager)
Self Referencing Binary M:N#
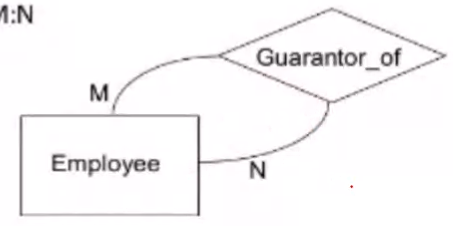
- Guarantor, Beneficiary are FK to the table Employee
The converted relational schema:
Employee(E#, Name, ....)
Guarantr(Guarantor, Beneficiary)
Ternary Relationship#
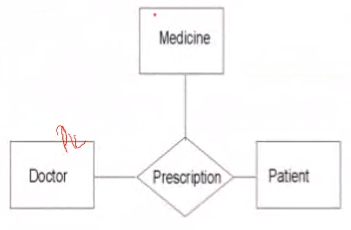
The converted relational schema:
Prescription (Doctor#, Patient#, Medicine#)
ER Constructs to relations:#
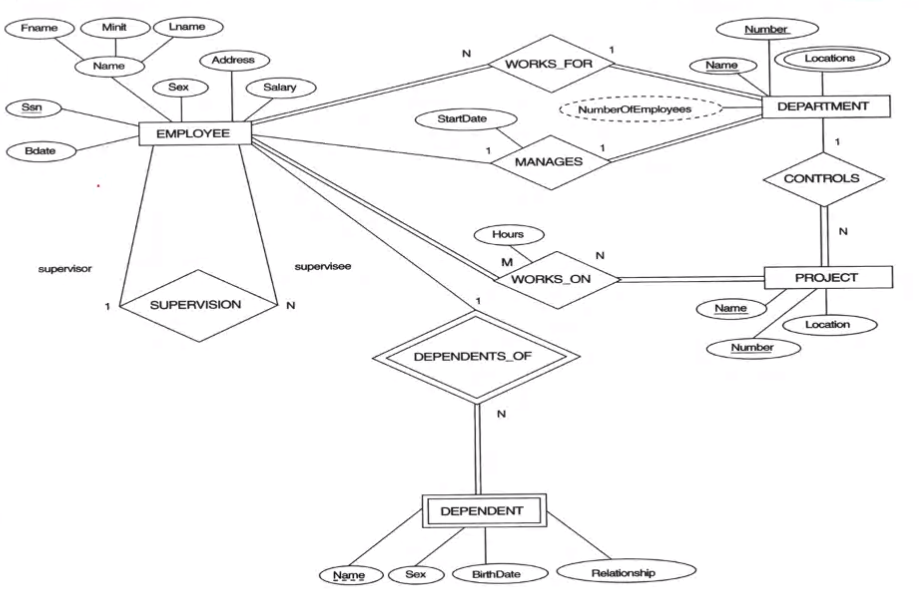
SuperSSN: FK to Employee table that shows supervisor
WorksOn: This relationship is it's own table since it is M:N
Supervising_DNO: FK to the Dept table that shows the supervising department
Works_For_DNO: FK to the Dept table that shows the supervising department
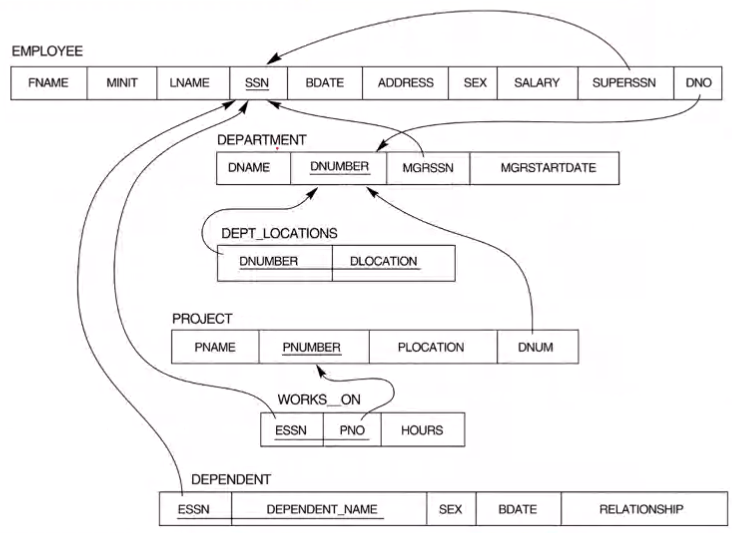
Employee(SSN, Name, Sex, .... , SuperSSN, Works_For_DNO)
Dept(DNO, Name, ManagerSSN, start_date)
Dept_locations(DNO, Location)
Project(PNO, Name, Location, Supervising_DNO)
Dependent(Name, Sex, DOB, Relationship Employee_SSN, )
WorksOn(PNO, SSN, hours)
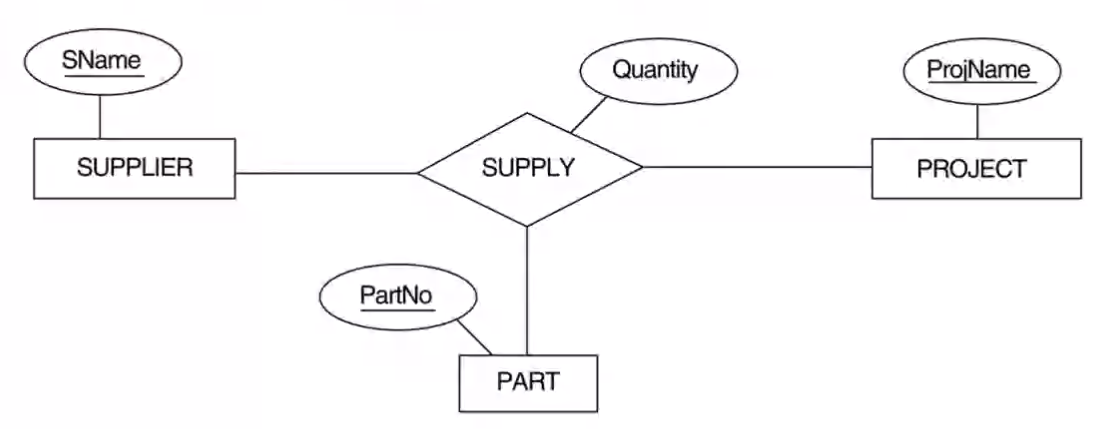
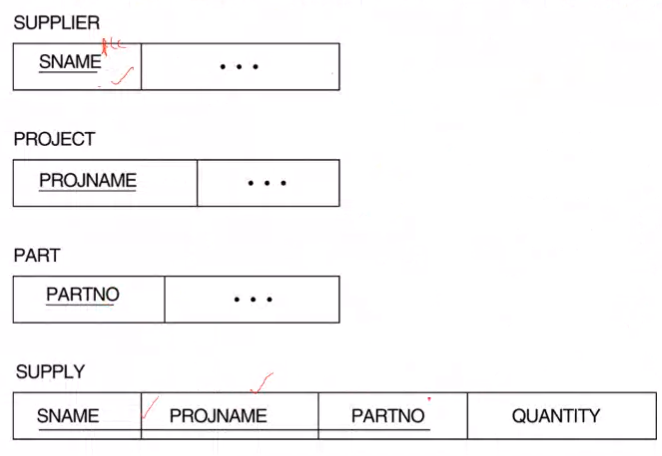
Ternary relationship conversion example:#
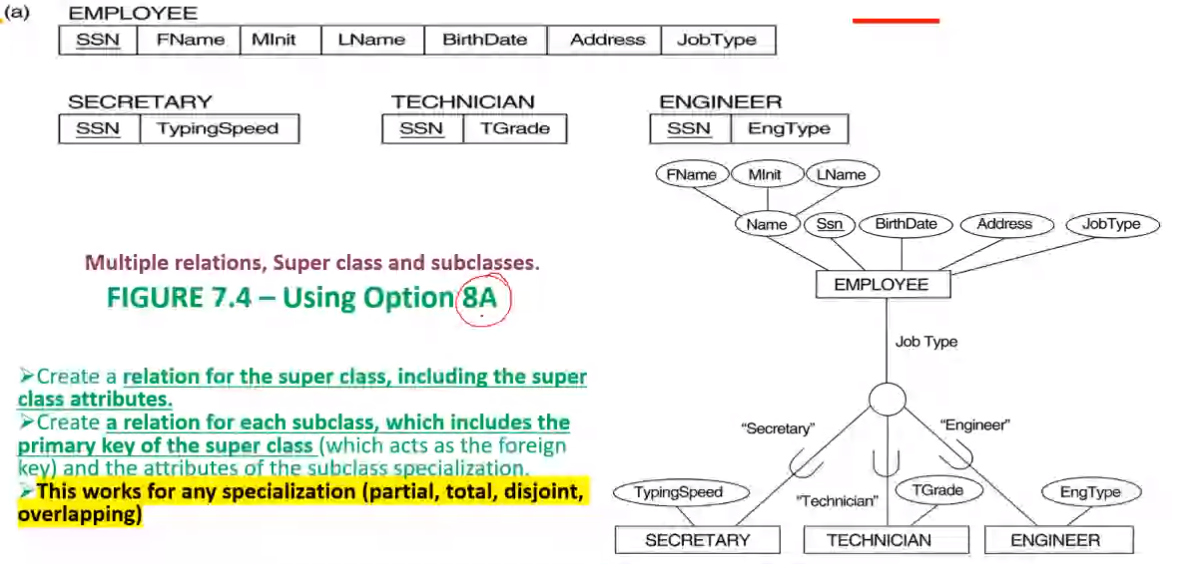
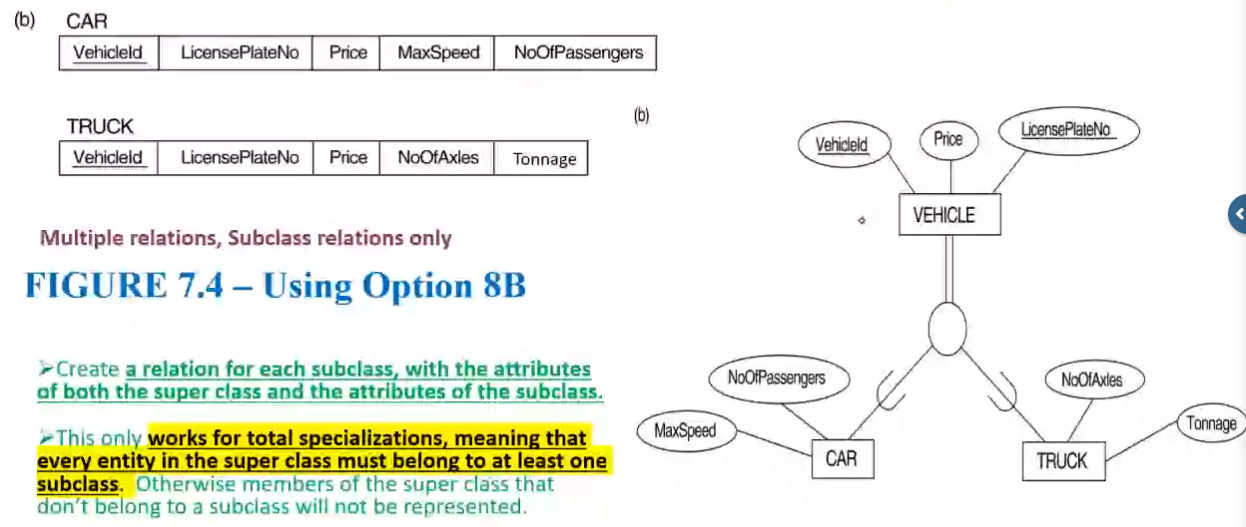
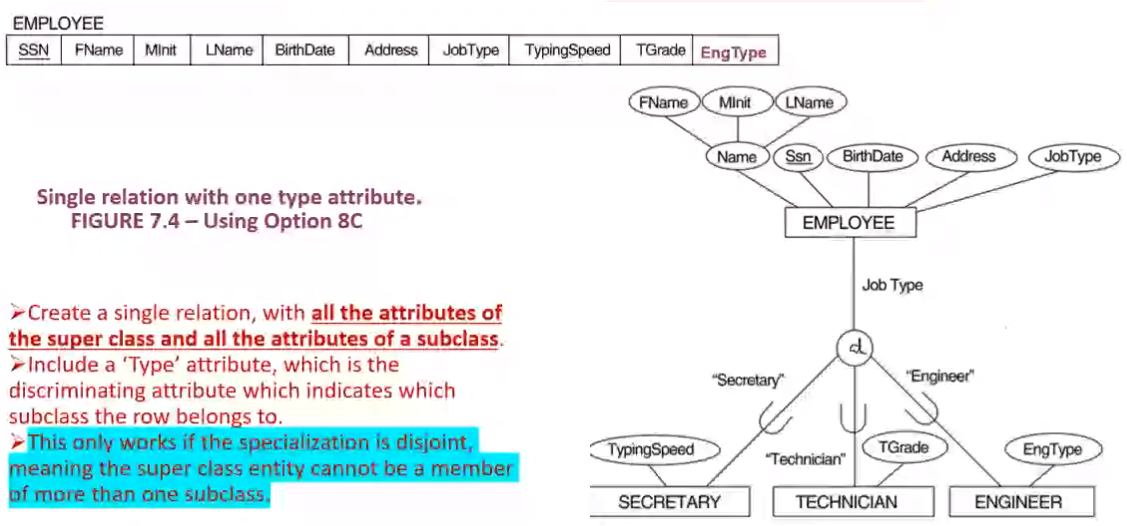
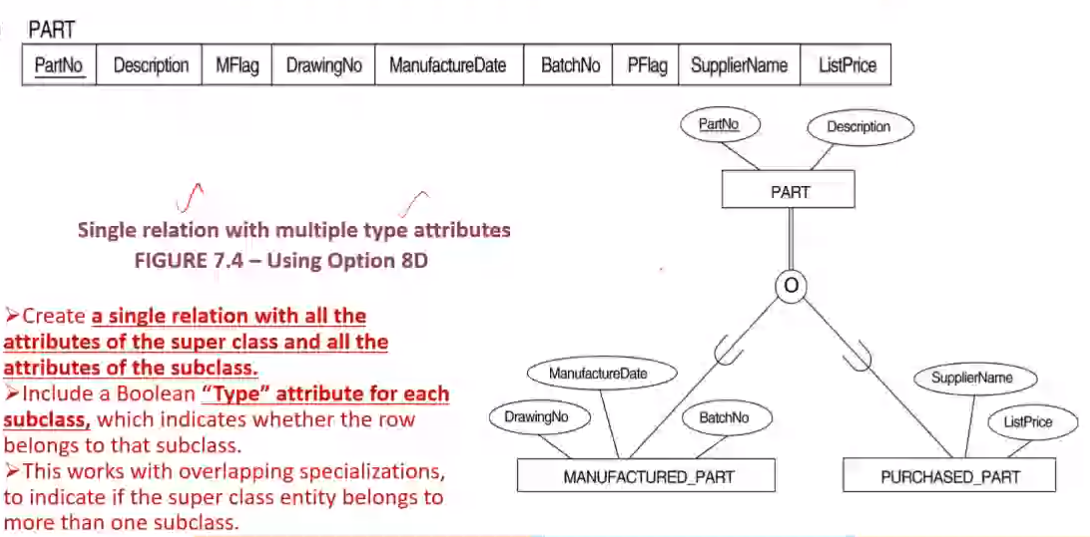
EER to Relational Mapping Steps#