Week 7#
Lecturer: Barsha Mitra, BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Date: 11/Sep/2021
Topics Covered#
- Deadlock Introduction
- System Model
- Wait-For-Graph (WFG)
- Knot
- AND Model
- OR Model
- Chandy Misra Haas Algorithm for the AND model
- Data Structures
- Steps
- Example
Deadlock Introduction#
- Deadlocks are explained in details here PreRecordedModule6#What is a deadlock
- A process may request resources in any order
- Request order may not be known apriori
- A process can request a resource while holding others
- If the allocation sequence of process resources is not controlled in such environments
- Deadlock condition where a set of processes request resources that are held by other processes in the set
System Model#
- N processors, N processes, each process runs on a prrocessor
- Systems have only reusable resources
- Processes are allowed to make only exclusive access to resources
- Only on copy/instance of each resource is present
- Process can be in two states
- Running
- Blocked
- Running state/active state:
- Process has all the needed resources
- Either is executing or is ready for execution
- Blocked state: Process is waiting to acquire some resource
Wait-For-Graph (WFG)#
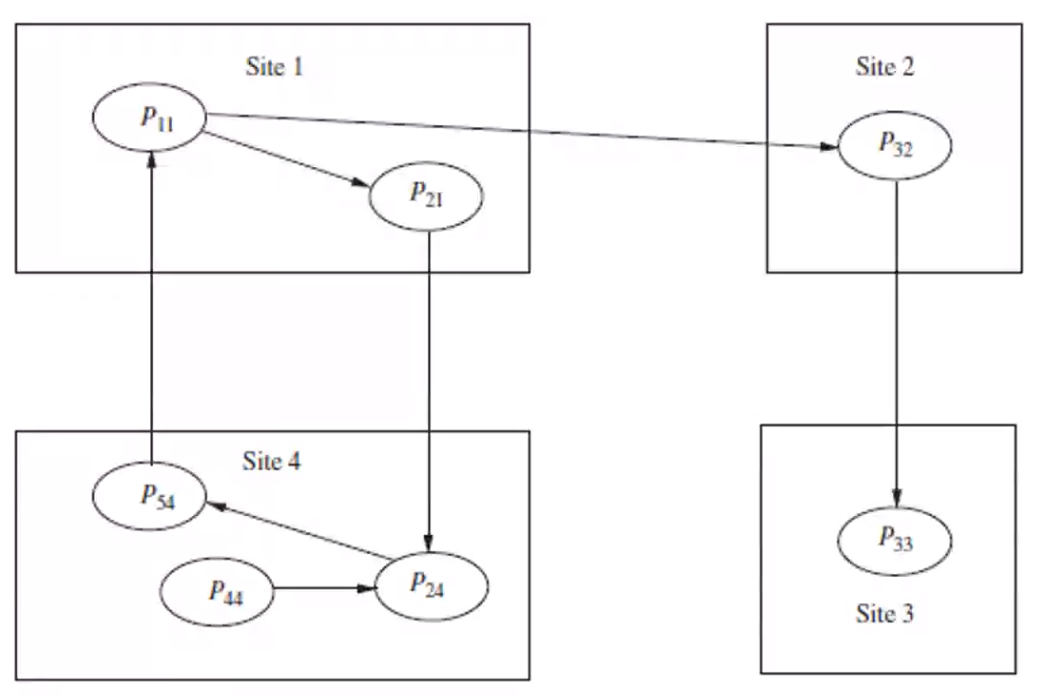
- State of a distributed system can be modeled as a directed graph
- Nodes are processes
- A directed edge from node \(P_1\) to node \(P_2\) if
- \(P_1\) is blocked
- \(P_1\) is waiting for \(P_2\) to release some resource
- A system is deadlocked if and only if there exists a directed cycle or knot in the WFG
Knot#
More info here PreRecordedModule6#Cycle Vs Knot
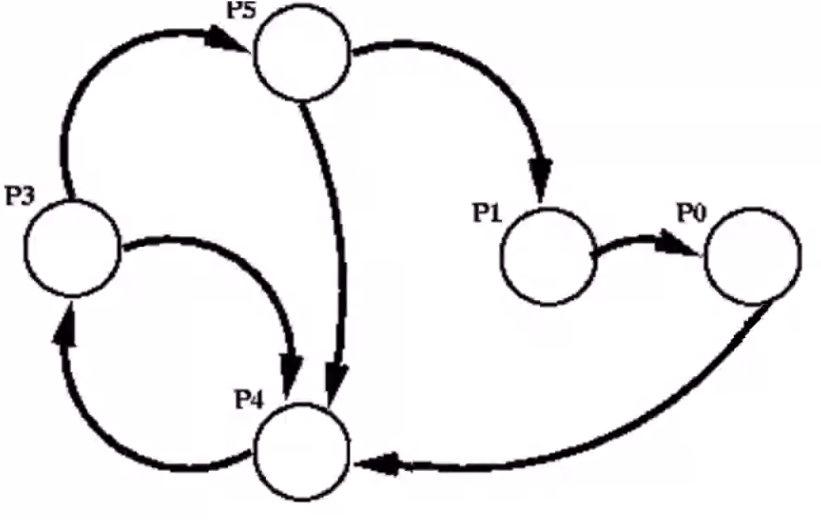
AND Model#
More details inn PreRecordedModule6#Cycle Vs Knot
In an AND graph a cycle is a sufficient condition to determine a deadlock
OR Model#
More details in PreRecordedModule6#OR WFGs and PreRecordedModule6#Cycle Vs Knot
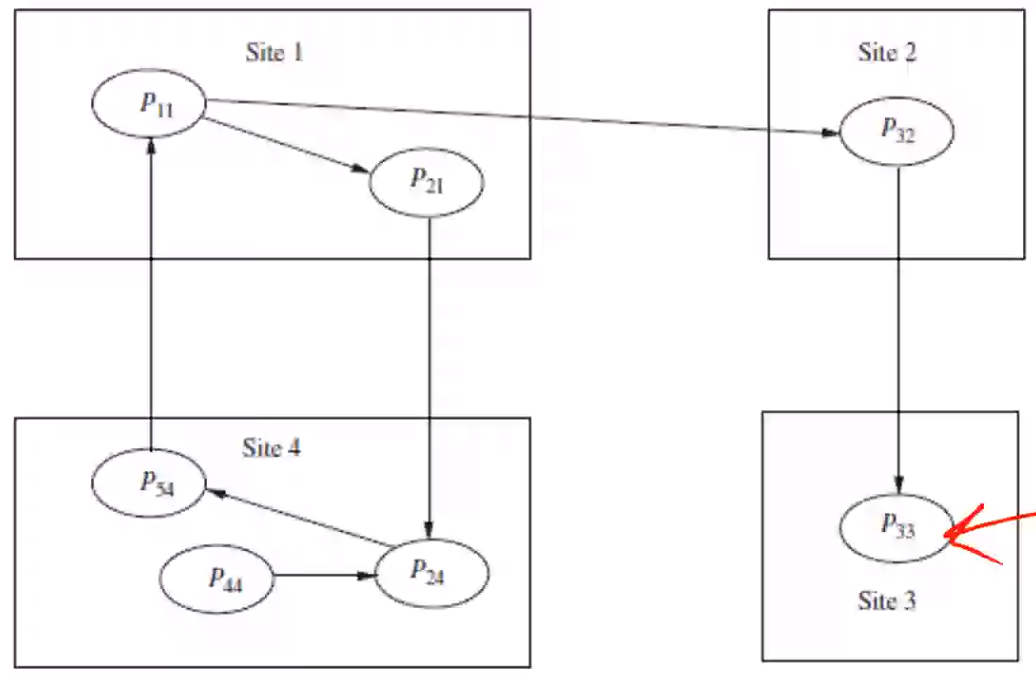
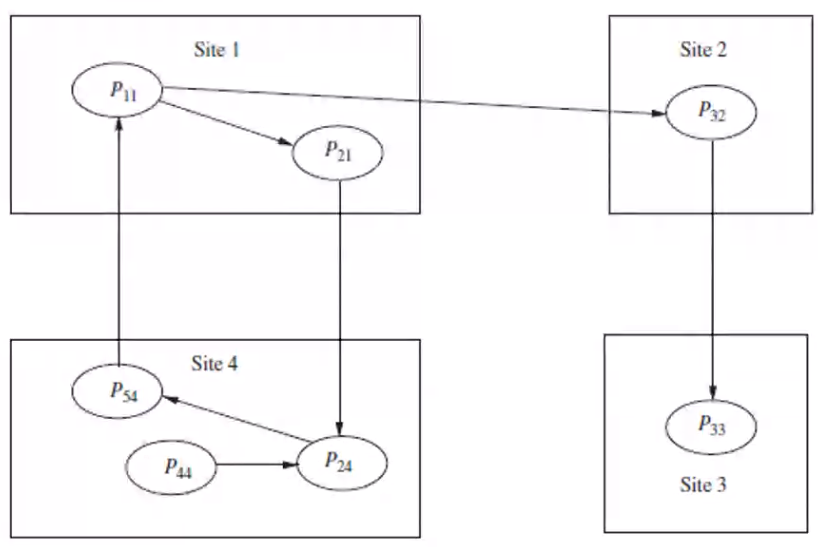
In an OR graph, a cycle is not a sufficient condition to determine a deadlock, we also need a knot
In the above diagram you can see that P_11 can satisfy its need by taking the resource used by P_33 and can change from Waiting to Active state.
Chandy Misra Haas Algorithm for the AND model#
Explained in detail here PreRecordedModule6#Chandy-Misra-Haas CMH Edge-Chasing for AND Graphs
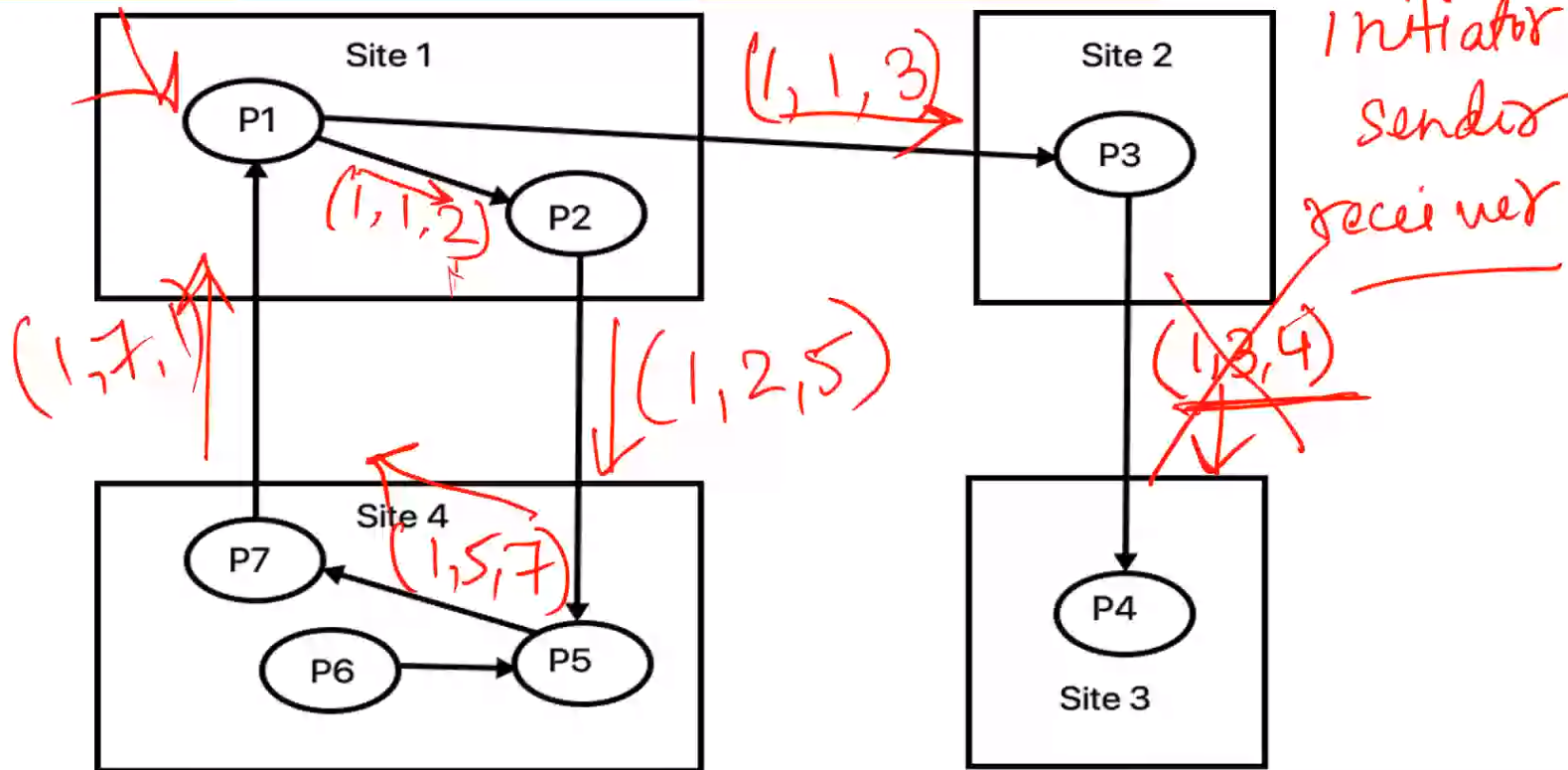
- Uses a special message called probe
- Probe is a triplet \((i, j, k)\)
- Denotes that
- It belongs to a deadlock detection initiated for \(P_i\) (1st element)
- It is sent by the site of \(P_j\)
- It sent to the site \(P_k\)
- Probe message travels along the edges of the global WFG graph
- Deadlock is detected when a probe message returns to the process that initialed it
Data Structures#
- Each process \(P_i\) maintains a bl=boolean array, \(dependent_i\)
- \(dependent_i(j)\) is \(TRUE\) if
- \(P_i\) knows that \(P_j\) is dependent on it
- Initially \(dependent_i(j)\) is false for all \(i\) and \(j\)
Steps#


Example#