Week 2#
Lecturer: Uma Maheswari, Faculty for BITS Pilani WILP
Date: 31/Jul/2021
Topics Covered#
- Intro to DBMS
- Advantages of DBMS
Mapping#
Traditional
Multimedia dbs
Geographical (GIS)
Data warehouses (OLAP) (analyze useful business information from very large databses, support descision making)
Real time and active DB
Time series db (volatile stocks/financial data)
Database design process#
Database design phases#
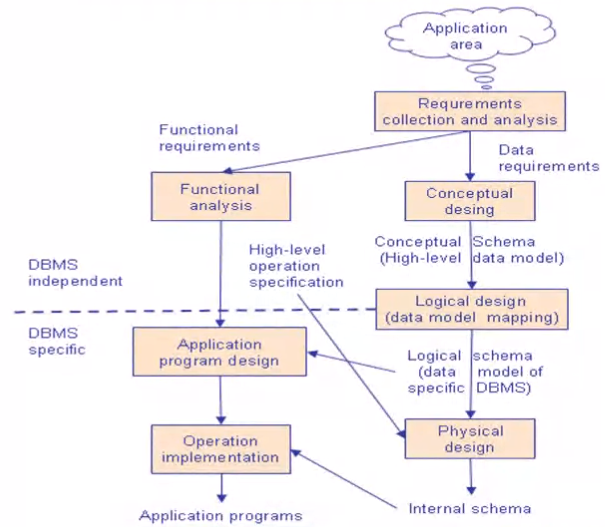
1. Requirements specification
1. Produces data reqs and functional reqs
2. Conceptual design
1. We develop an ER model or UML class diagram
2. We describe different entities, their relation and their attributes
3. Logical design
1. Based on the ER diagrams created, the designers create
2. Primary and foreign keys are determined
3. Normalization is to eliminate redundancy and potential update anomalies.
4. Physical design
1. This phase is to develop the database
2. Decide the datatypes
3. The SQL clauses are written to ccreate the DBs
Example:


Conceptual database design#
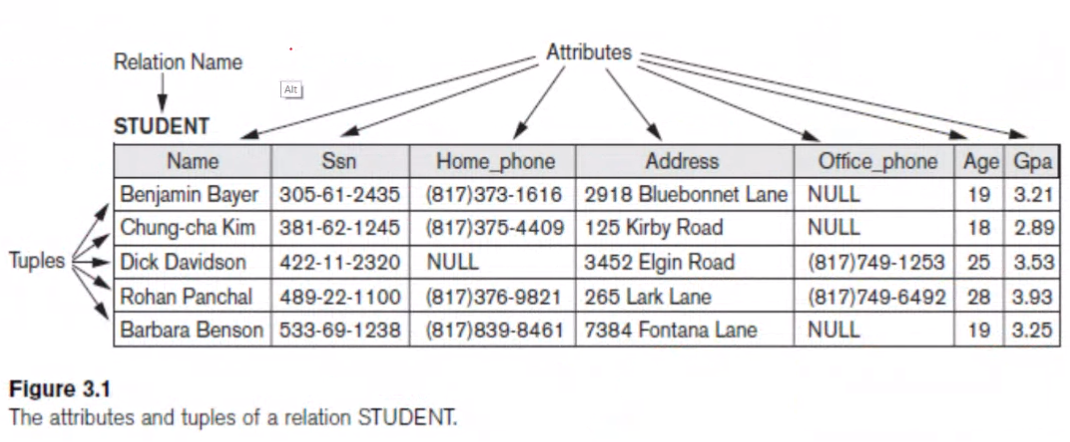
Domains, Atttributes, Tuples, and Relations#
Entity Relationship Diagram#
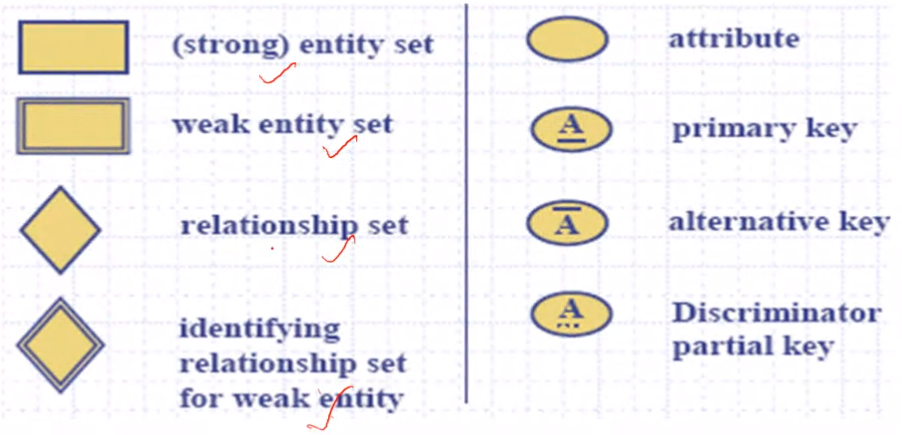
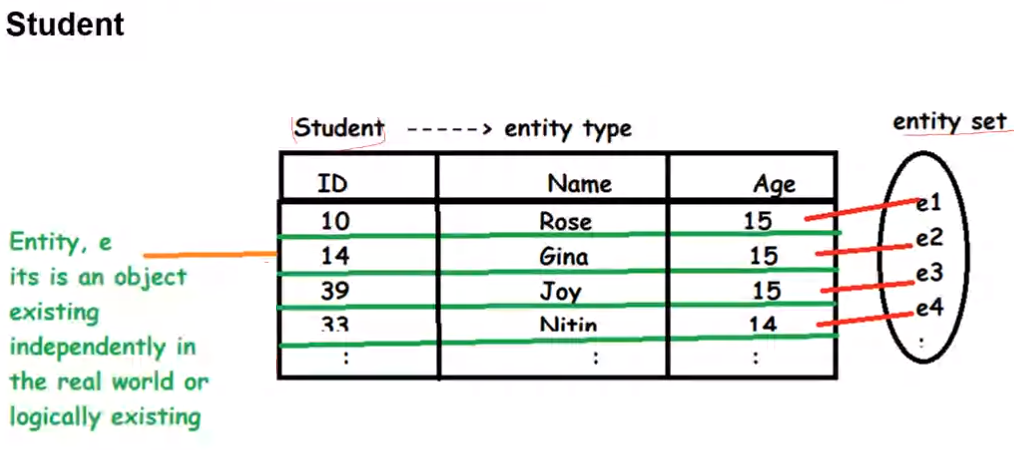
Entity in ER#

Example of Entity#
Attributes in ER#

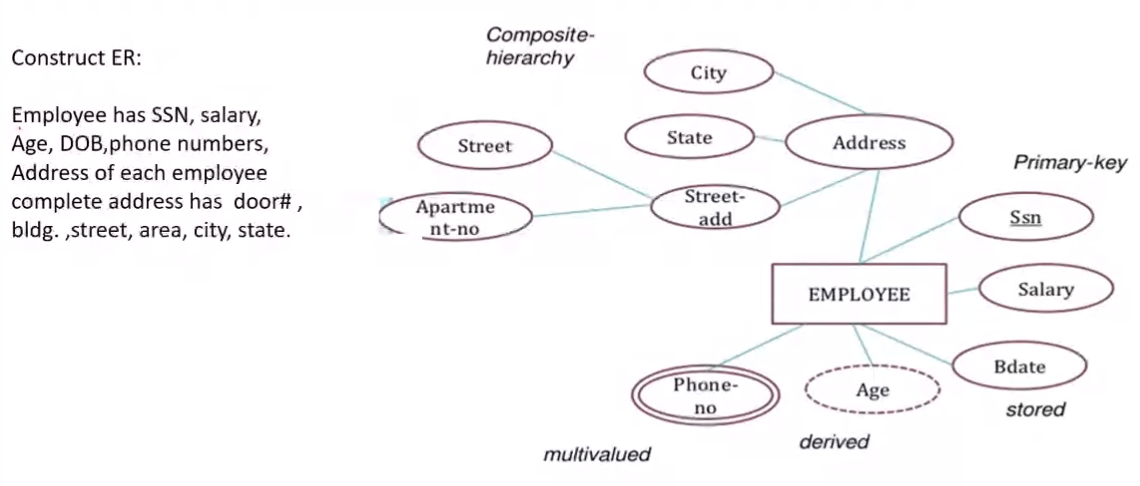
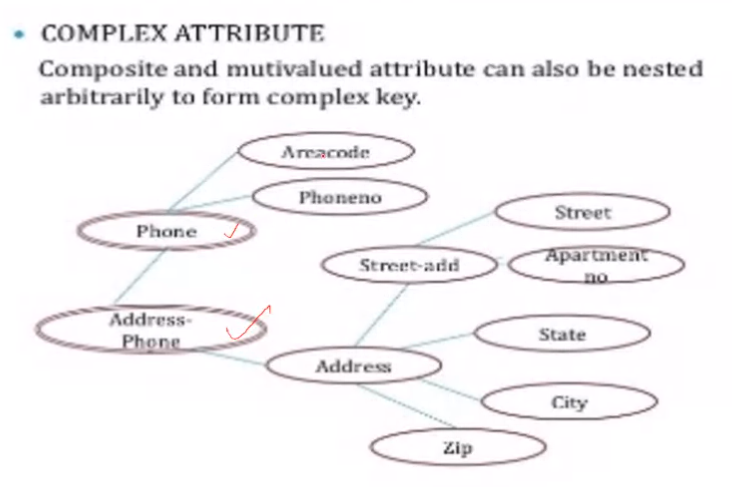
- Simple and composite:
- Simple cannot be split, it is atomic
- Composite can be divided into smaller sub parts (It is a combination of simple attributes example address)
- Single valued and multivalued:
- Single valued means there is only one value for that column (Example name)
- Multivalued means there are more than one value for that column (Example Phone numbers)
- Stored attributes and Derived attribute:
- Attributes from which other attributes can be derived is a stored attribute (Example birth date, job join date) This will be stored in the DB
- Derived attribute are attributes that are derived from stored attributes (Example age from birth date, experience from job joining date) This value would not be stored in the DB
- Key Attributes

Relationship between the physical design to the conceptual design#
- Table -> Entity Type
- Row → Entity/Tuple
- Column → Domain
- Set of all rows → Entity Set
Drawing attributes#
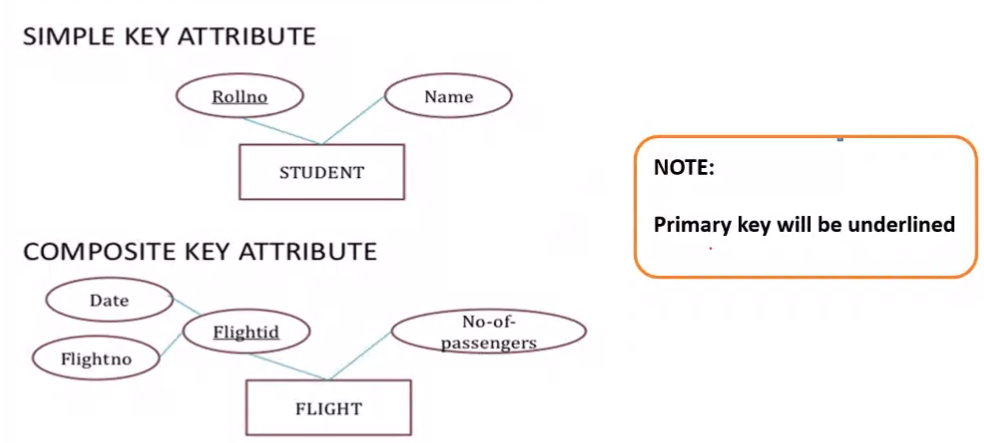
flightid: Composite id and single valued
Rollno: key attribute since every STUDENT will have a unique value