Week 9#
Lecturer: Barsha Mitra, BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Date: 24/Oct/2021
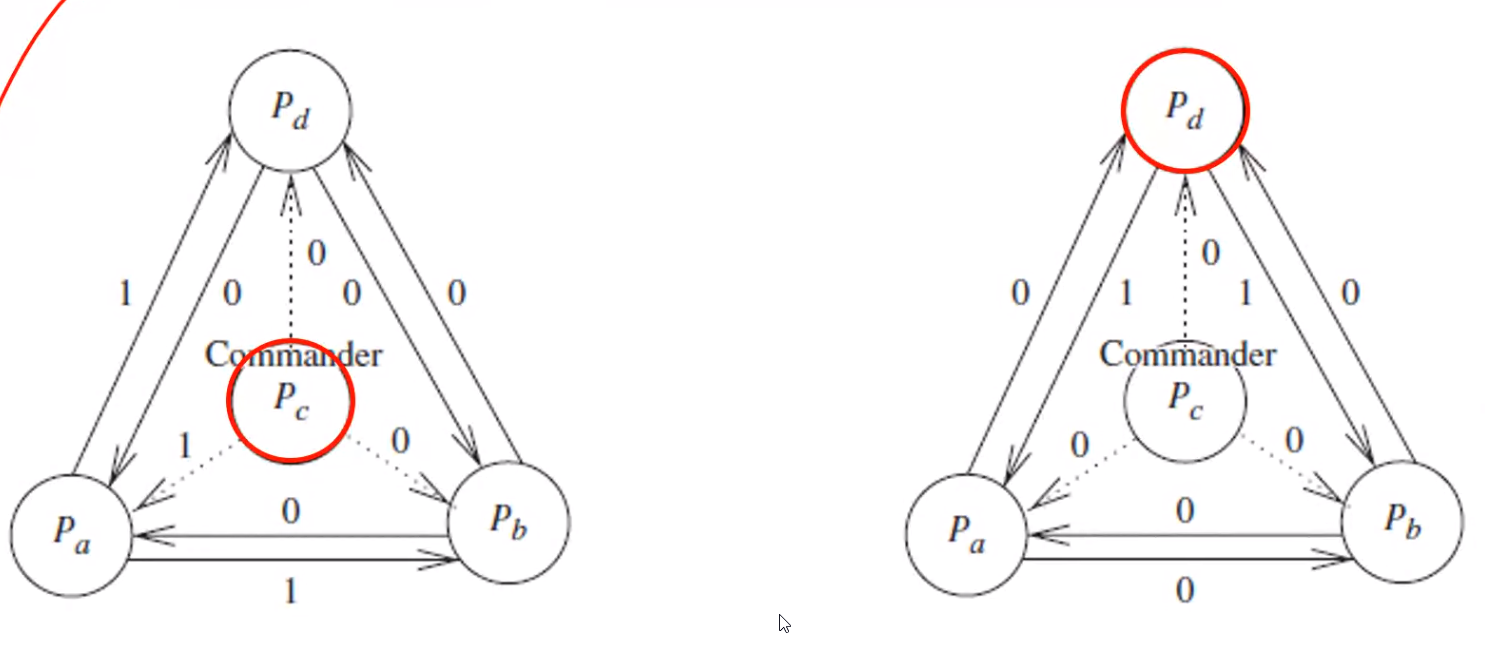
Byzantine Agreement Problem#
Assumptions made#



\(n = 4\)
\(f = 1\)
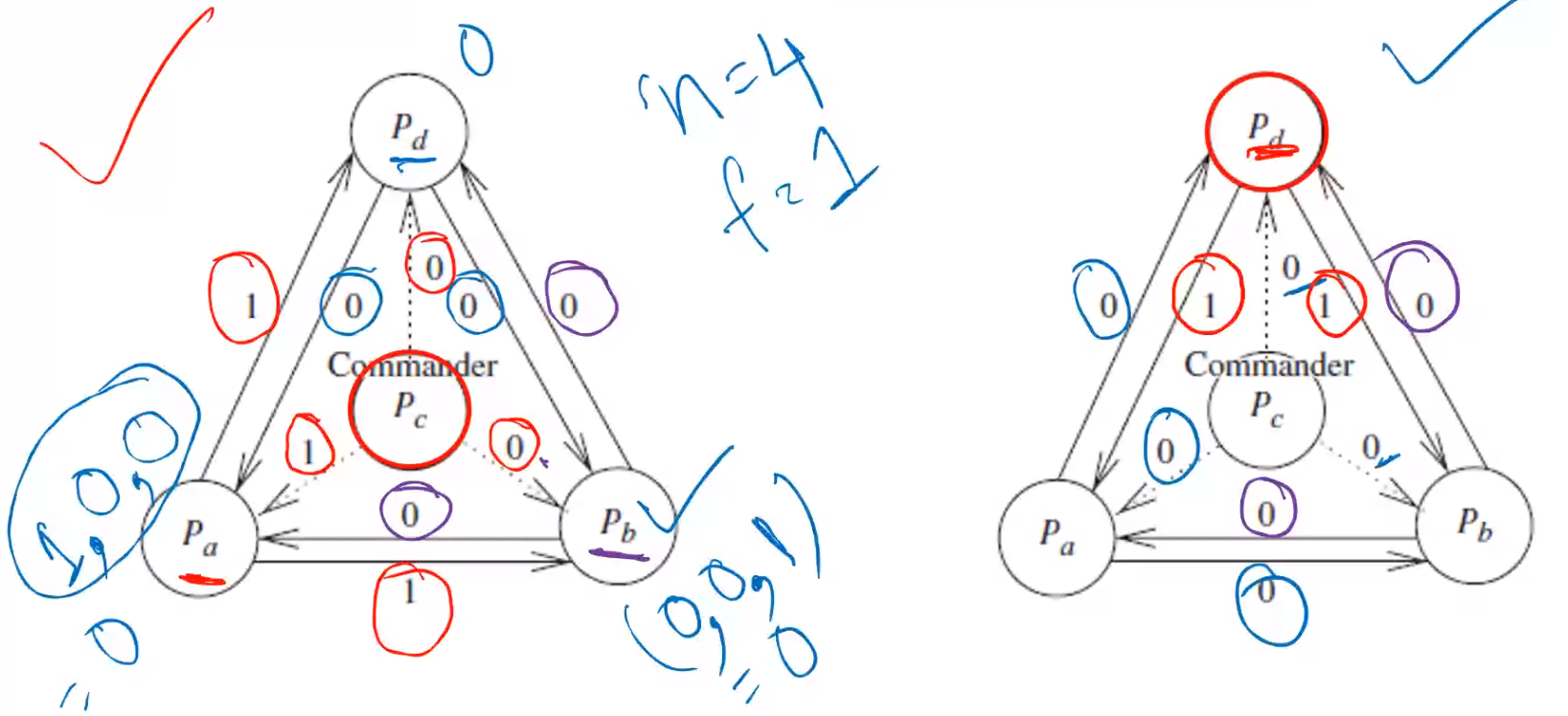
Byzantine Agreement Tree Algorithm: Recursive Formulae#

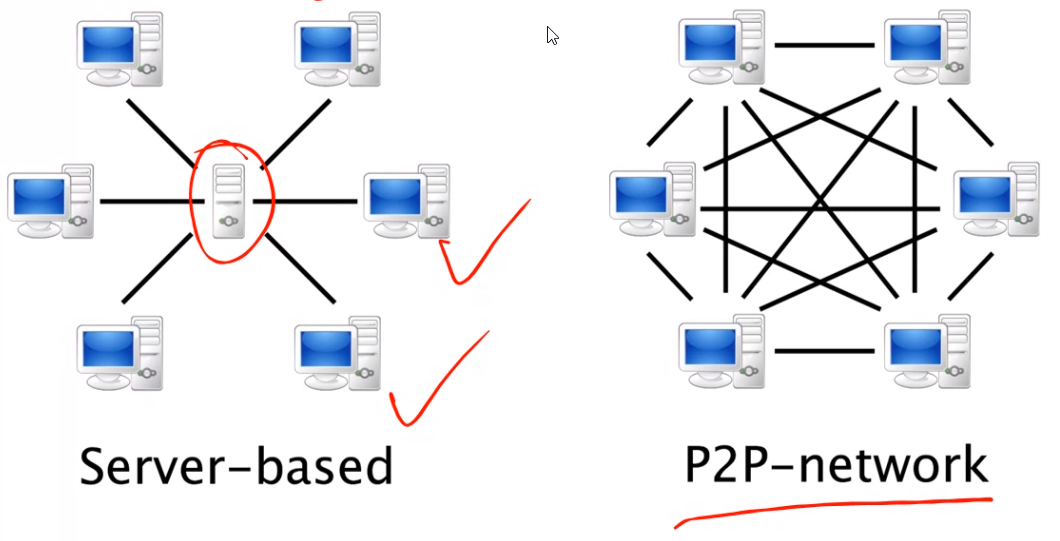
Peer to Peer Network#

Well known P2P networks#
- Napster
- Gnutella
- Freenet
- Pastry
- Chord
- CAN
Introduction to P2P networks#
- P2p networks allow the location of arbitrary data objects
- impose a low cost for scalability, and for entry into an exit from the network
- Ongoing entry and exit of various nodes and dynamic insertion and deletion of objects is termed as churn
- Impact of churn should be as transparent as possible
Data Indexing and Overlays#
Centralized Indexing:#
- Use of one or a few central servers to store references to the data on many peers
- Napster uses centralized indexing
Local Indexing#
- Requires each peer to index only the local data objects
- Remote objects need to be searched for
- Used in unstructured overlays
- Gnutella uses local indexing
Disctributed Indexing
- Involves the indexes to the objects at various peers being scattered across other peers throughoput the P2P network
- Disctributed indexing is the most challenging of the indexing schemes
- Many novel mechanisms have been proposed, most notably the disctributed hash table (DHT)
Structured Overlays#

Unstructured Overlays#

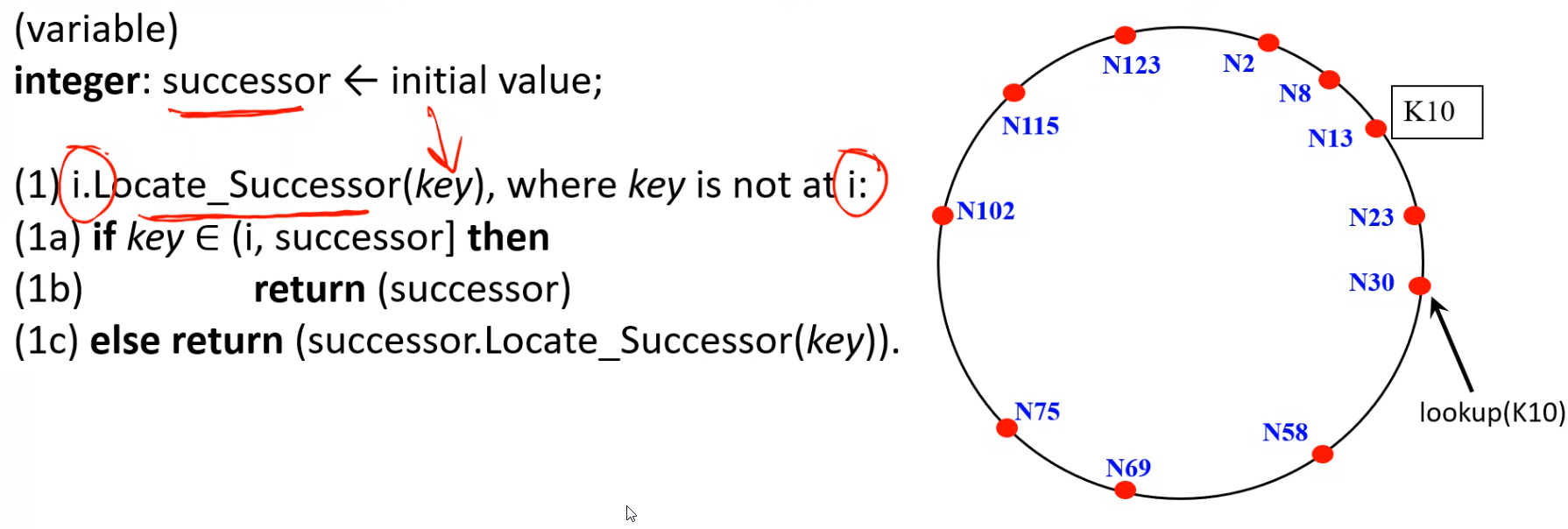
Chord Distributed Hash Table: Overview#
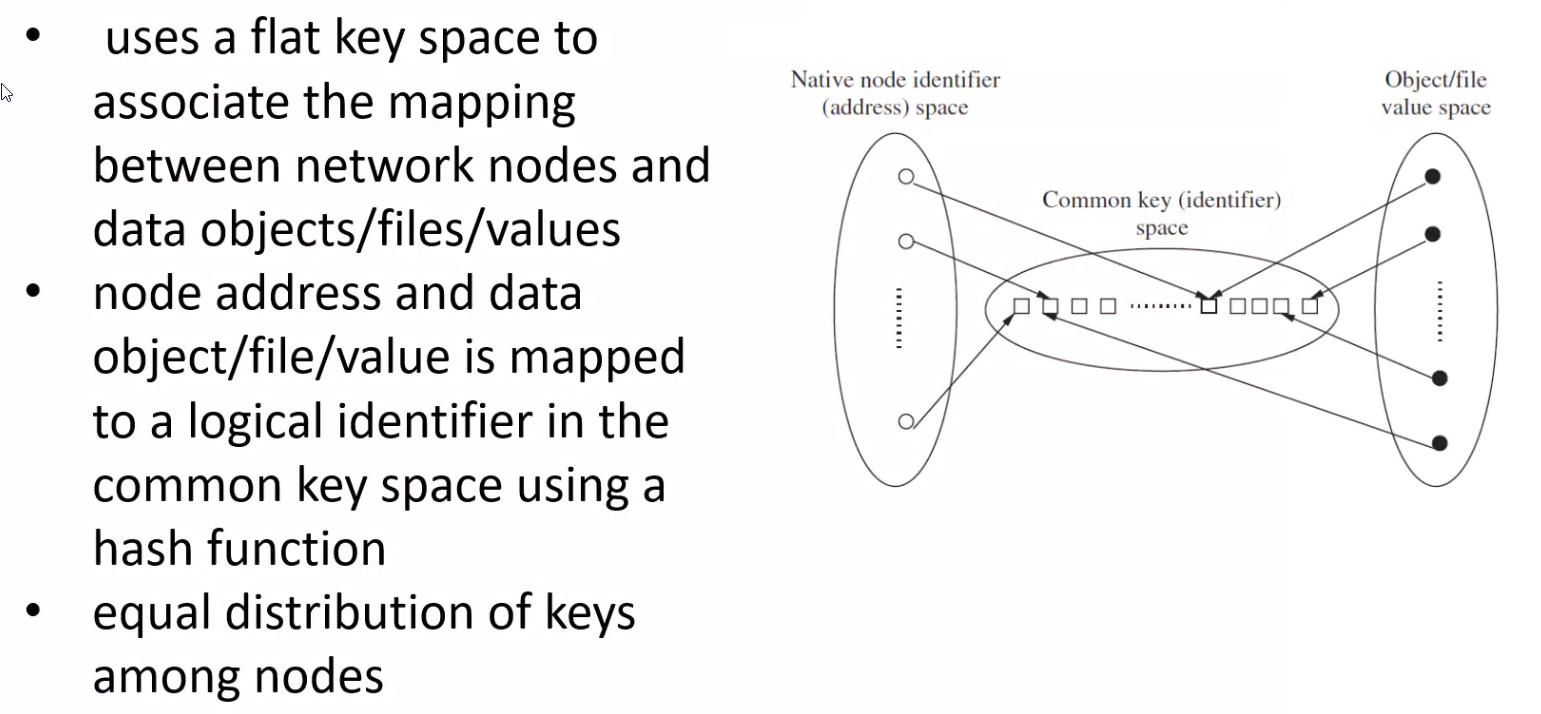


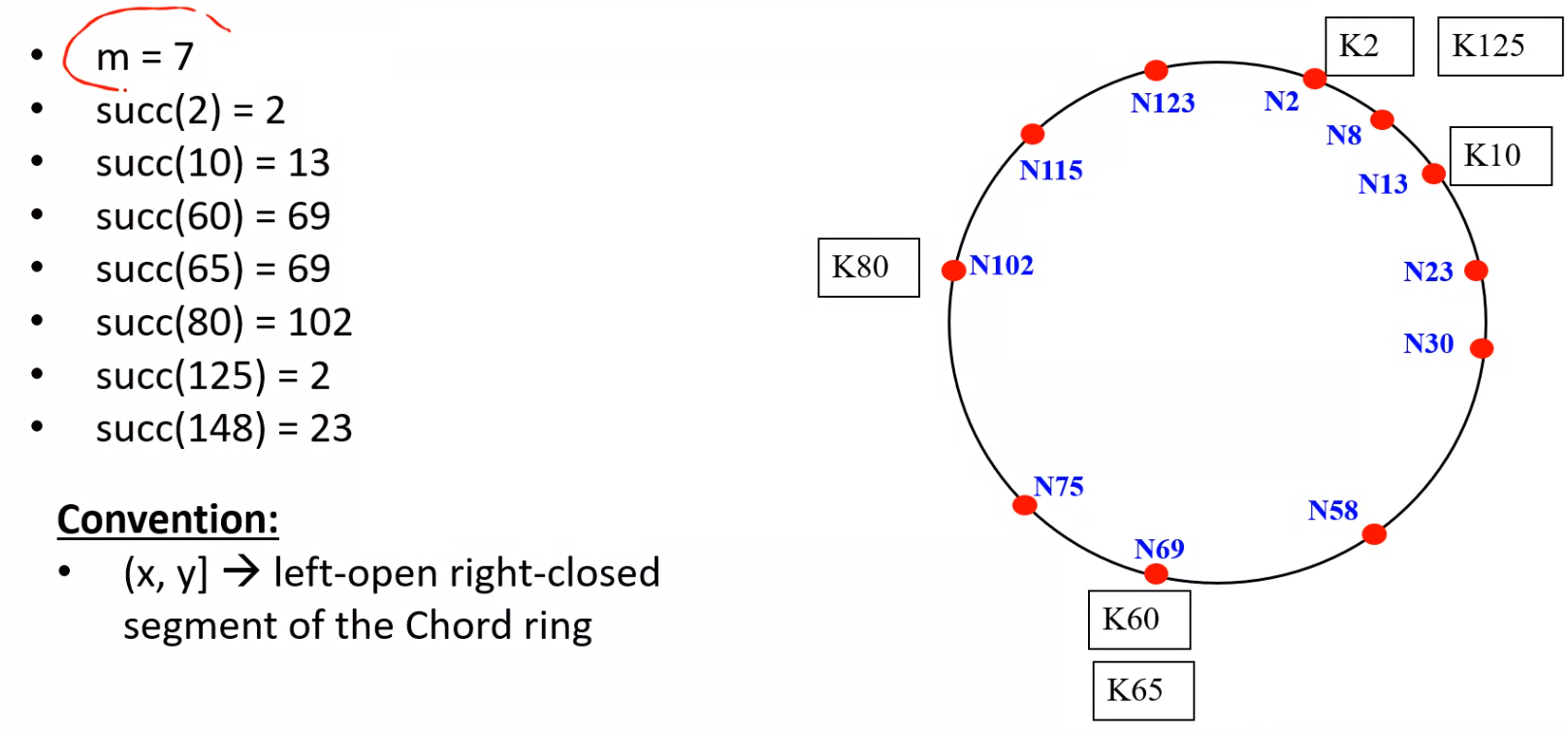
Simple Lookup#