Module 2#
Availability#
Availability General Scenario#

Sample Concrete Availability Scenario#
The heartbeat monitor determines that the server is non responsive during normal operations. The system informs the admin when the heartbeat stops. Check the following for more info Module2SA#Module 2#Availability Tactics#Detect Faults
Goal of Availability tactics#
Availability Tactics#
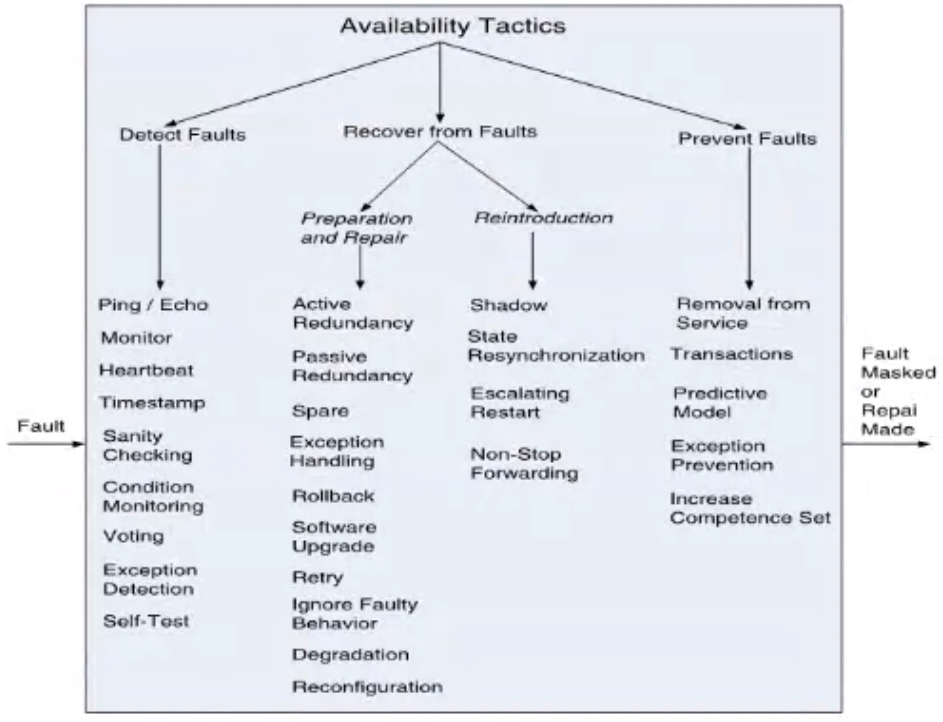
Detect Faults#
- Ping/echo: asynchronous req/res message pair exchanged between nodes, used to determine reachability and the round trip delay through the associated network path
- Monitor: A component used to monitor the state of health of other parts of the system. A system monitor can detect failure or congestion in the network or other shared resources such as from a denial of service attack
- Heartbeat: a periodic message exchange between a system monitor and a process being monitored
- Timestamp: Used to detect incorrect sequences of events, in distributed message passing systems
- Sanity Checking: Checks the validity or reasonableness of a component's operations or outputs; typically based on a knowledge of the internal design.
- Condition Monitoring: Checking conditions in a process or device, or validating assumptions made during the design.
- Voting: to check that replicated components are producing the same results. Comes in various flavors: replication, functional redundancy, analytic redundancy. Example is height calculation in an aircraft. There are several ways we can determine this, we now vote all these results and check against a particular tolerance and when the majority of the values are within that then we can choose that value and determine the component that is failing.
- Exception Detection: detection of a system condition that alters the normal flow of execution, eg system exception parameter fence, parameter typing, timeout.
- Self test: procedure for a component to test itself for correct operation.
Recover From Faults#
- Active redundancy (Hot spare): A spare processes inputs just like the active one so that the spares are synchronous in case of failure
- Passive redundancy (Warm spare): Only active nodes process inputs and the spares are brought up when the active ones fail
- Spare (Cold spare): Redundant spares are OOS until a failure happens at which point a power on reset procedure is initiated on the spare prior to its being placed in service
- Exception handling: dealing with the exception by masking it by correcting it
- Rollback: Revert to a previous known good state.
- Software Upgrade: in service upgrades to executable code images in a non service affecting manner
- Retry
- Ignore Faulty Behavior: For example ignoring spurious messages that can cause failure
- Degradation
- Reconfigure
- Shadow: operating a previously gfailed or in service upgraded component in a shoadow mode for a predefined time prior to reverting the component back o an active role
- State resync
Prevent Faults#
- Escalating restart: recover from faults by varying the granularity of the components restarted and minimizing the level of service affected
- Non stop forwarding: Functionality is split into supervisory and data.
- Removal from service: Temporarily placing a system in an OOS state for the purpose of mitigating potential system failures
- Transactions: bundling state updates so that async messages exchanged between distributed components are atomic, consistent isolated and durable
- Predictive model: monitor the state of health of a process
- Exception Prevention: preventing system exceptions
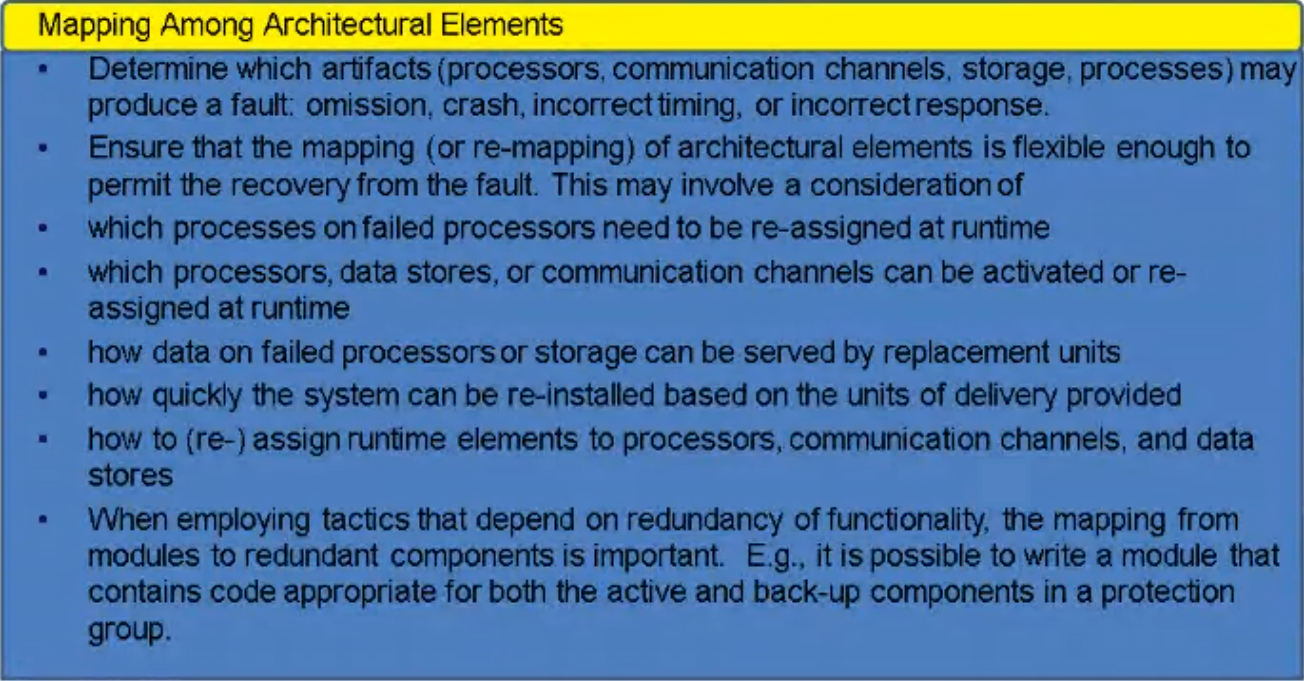
Design Checklist for Availability#





Usability#
- Usability is concerned with how east it is to accomplish a desired task by the user
- A focus on usability is the cheapest and easiest ways to improve a systems quality.
- Usability comprises of:
- Learning system features
- Using a system efficiently
- Minimizing impact of errors
- Adapting to failures
Usability General Scenario#

POS Terminal#
- Actors:
- Cashier
- Customer
- Supervisor
High level vs low level goals#
- log out: Secondary goal
- Handle payment: Primary goal
- Negotiate contract with supplier: Very high level goal
These use cases are at different levels, and are the all valid
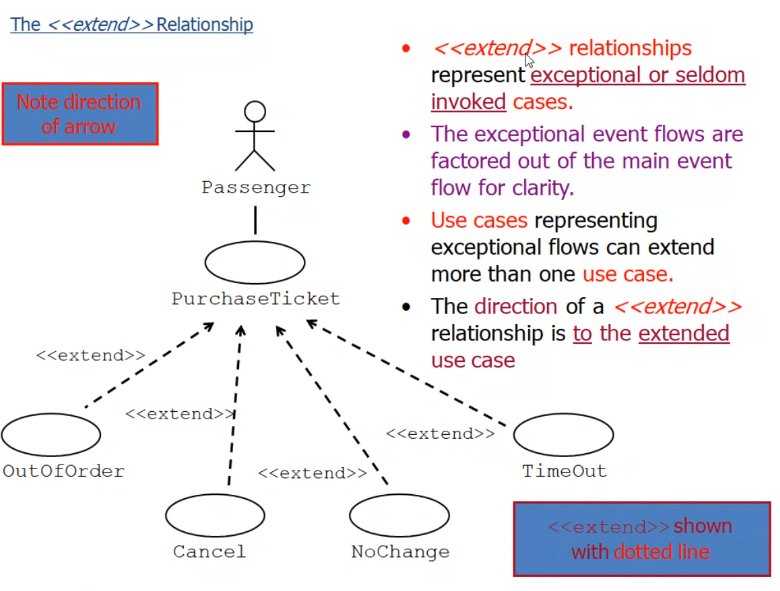
Extends relationship#
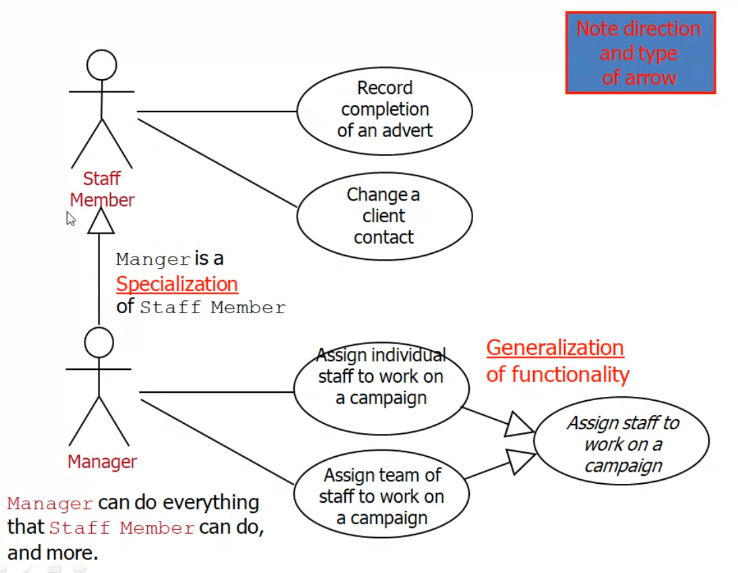
Specialization relationship#
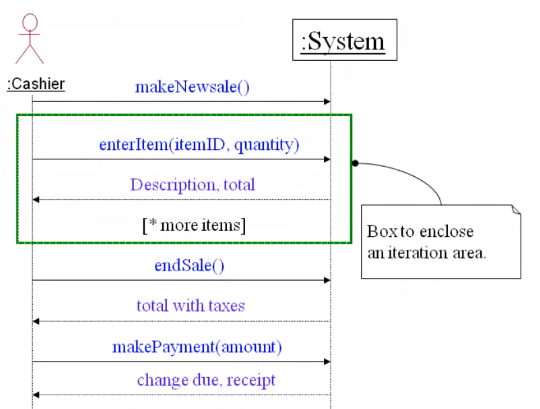
Drawing System Sequence Diagrams#
Example POS terminal Process Sale scenario
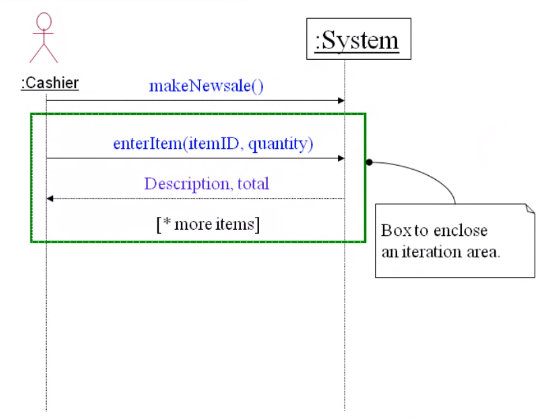
Iterations are enclosed in one box

Domain Model#

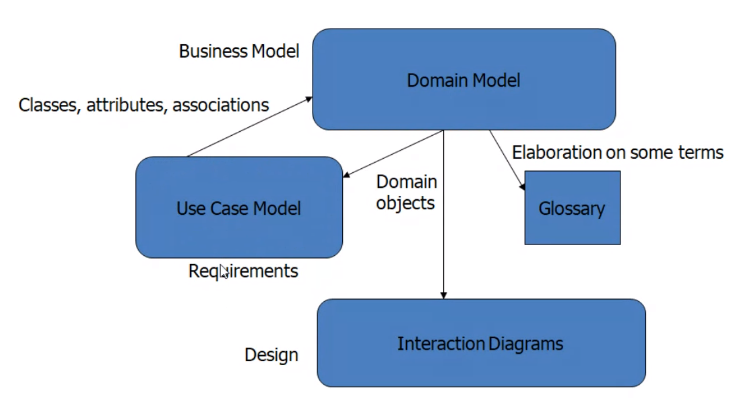
Finding concepts#
