Week 3#
Lecturer: Uma Maheswari, Faculty for BITS Pilani WILP
Date: 07/Aug/2021
Topics Covered#
- Answer to questions from previous class
Answer to questions from previous class#
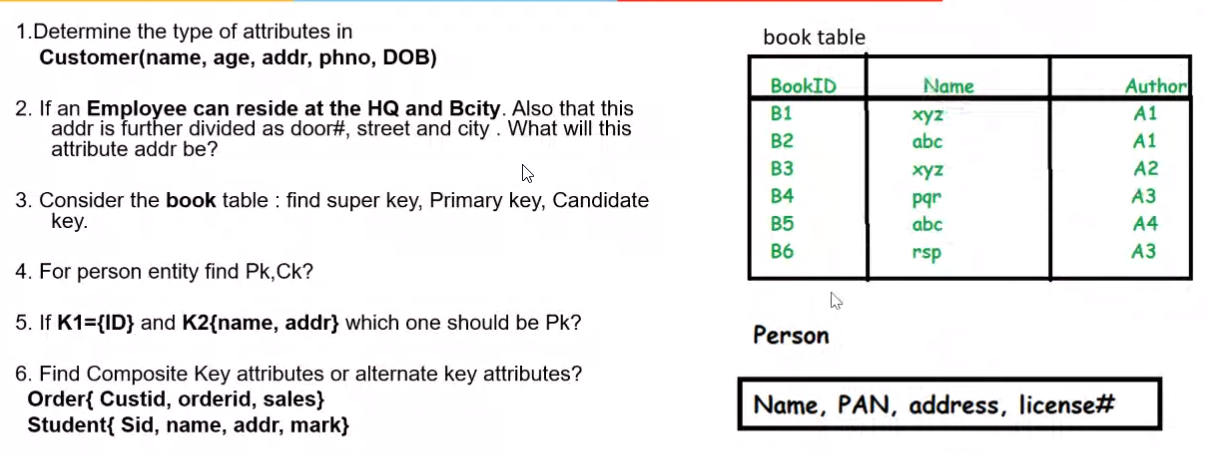
Q1: Answer
Name -> Simple
Age -> Derived
addr -> Composite
pho -> Simple, Multi Valued
DOB -> Stored
Q2: Answer
Since there are two addresses, the attribute is multivalued. and since the address itself is a composite attribute, the Employee addr is a composite multivalued
Q3: Answer
We know that \(P_k \in C_k \in S_k\)
1. Super Key \(S_k\) -> BookID, BookID-Name, BookID-Author, Name-Author, BookID-Name-Author
2. Candidate Key \(C_k\) -> BookID, Name-Author
3. Primary Key \(P_k\) -> BookID
Q4: Answer
1. Candidate Key \(C_k\) -> PAN, Licence#-address
2. Primary Key \(P_k\) -> PAN
Q5: Answer
K1 is the Pk since it has the least composition
Q6: Answer
Composite Key attributes -> Custid-orderid, Name-addr
Relationship#
In the above diagram, the two entities are having the relationship 'works for'.
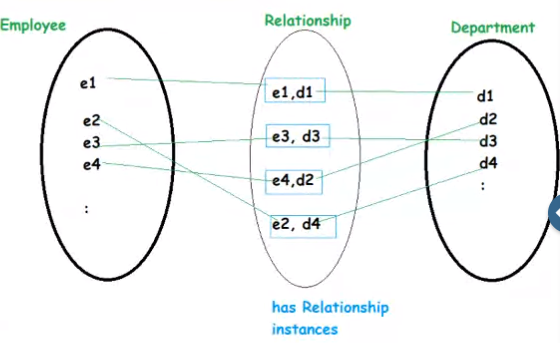
Relationship Properties#
Degree of relationship#
In the above example the degree of the SELLS relationship is 3
In the above example the degree of the Works For relation is 2
The above relation is a unary relationship where the relationship is with itself
Role Name#
In case of Unary relationship, we give a role name to the entities. For example in the supervision relationship, there are some employees who are supervisor and some will be supervisee. Here supervisor and supervisee are the role names
Mapping Constraints#
Cardinality Constraints#
-
1 to 1 relationship
graph LR A[Employee]-- 1 ---B{Manages} B-- 1 ---C[Department] -
N to 1 relationship
graph LR A[Employee]-- N ---B{Works For} B-- 1 ---C[Department]
N employees work on -
M to N relationship
graph LR A[Employee]-- M ---B{Works On} B-- N ---C[Projects]
M employees can work on 1 project or 1 employee can work on N projects
Participation Constraints#
- How many people are participating in a relationship
- Total Participation
graph LR A[Employee]-- N ---B{Works For} B-- 1 ---C[Department] - All employess participate in a department
- But not all departments need to have
- \(Cardinality + Optionality = multiplicity\)
Relationship with attributes:#
Consider the following 1 to 1 case:
Start date attribute can show when the employee managed a department, hence the start date can be in either of the entity set
Consider the following N to 1 case:
Here start date is associated to every employee , since start date is unique for every employee but not the other way around, start date can be in employee table.
Consider the following M to N case:
In the above case, the hour data must be in the relationship table since it cannot be associated to either employee or a project tables.
MIN-MAX constraint#
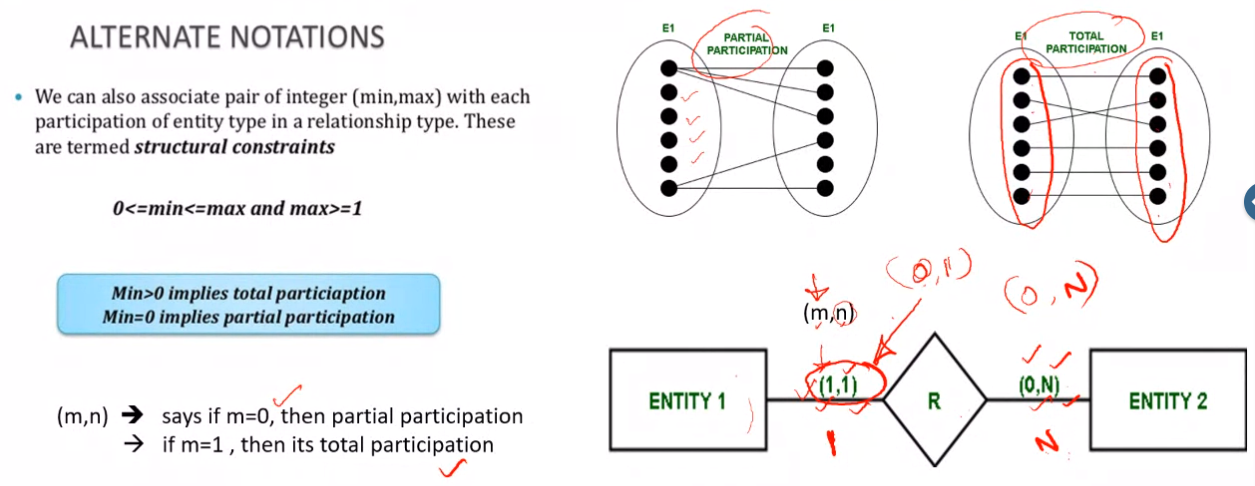
In the above relation min-max form for Employee is {1,N} and for department is {0,1}
Entity Types#
Weak and Strong#
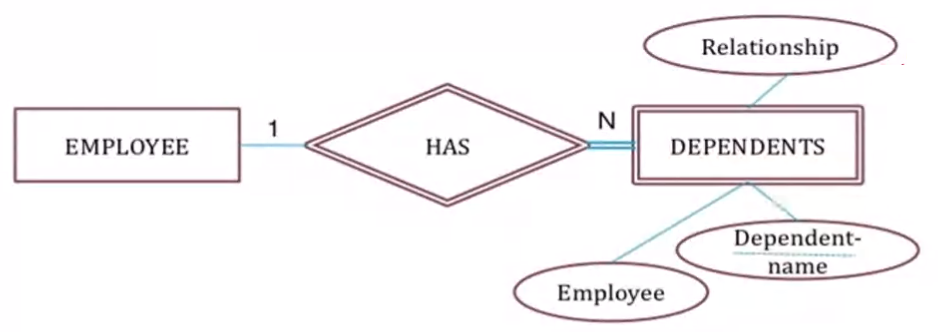
- An entity that does not have a key attribute is a weak entity (Denoted by double rectangle)
- And a strong one has a key
- A double diamond relationship denotes a relationship between a strong and weak entity
- In the above example the Dependents entity does not have a key, hence it uses the employee id as the key
- Driver license entity cannot exist without person entity
ER Model#
Refinement
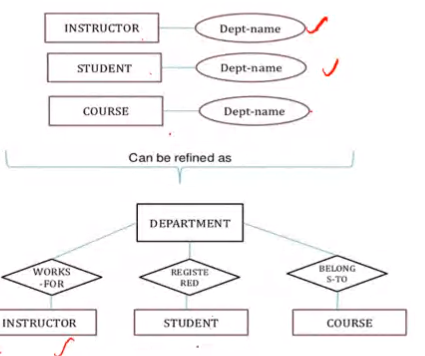
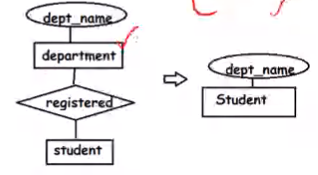
Invese refinement
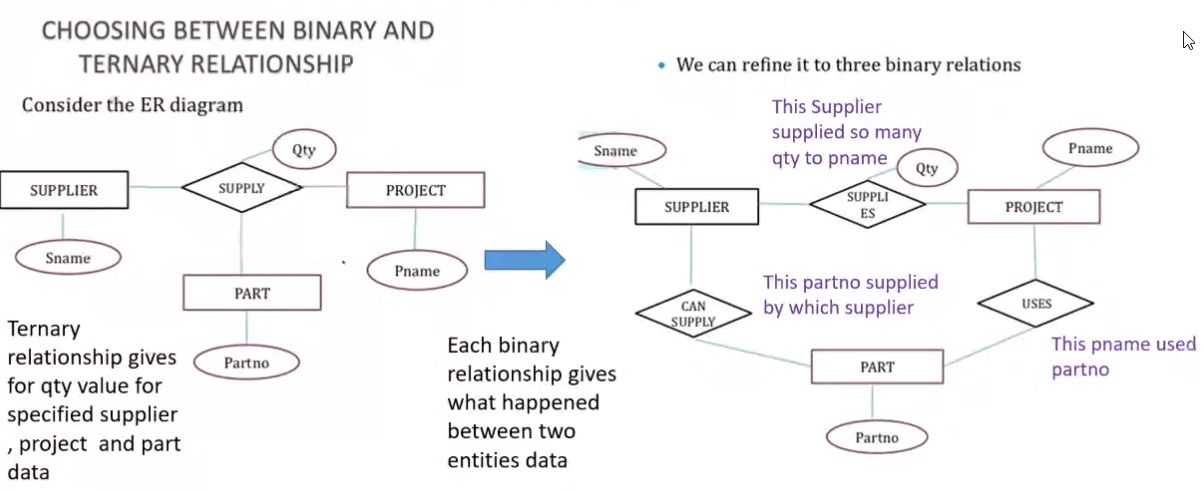
Binary and Ternary Relationships#
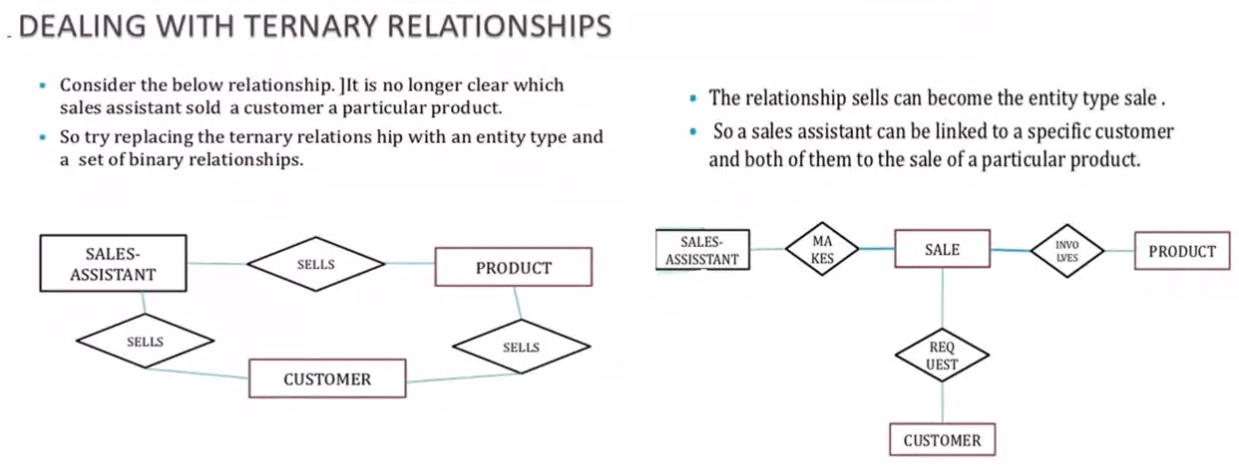
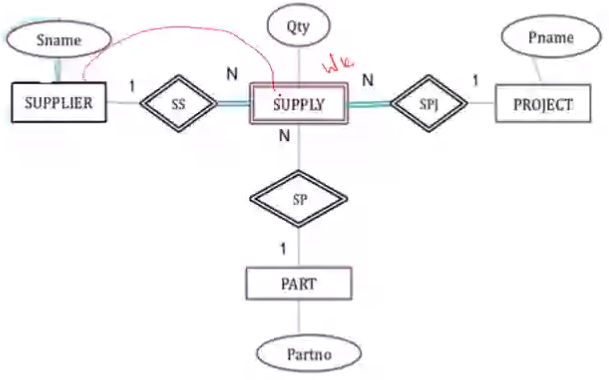
Example of entities having more than 1 relationships#
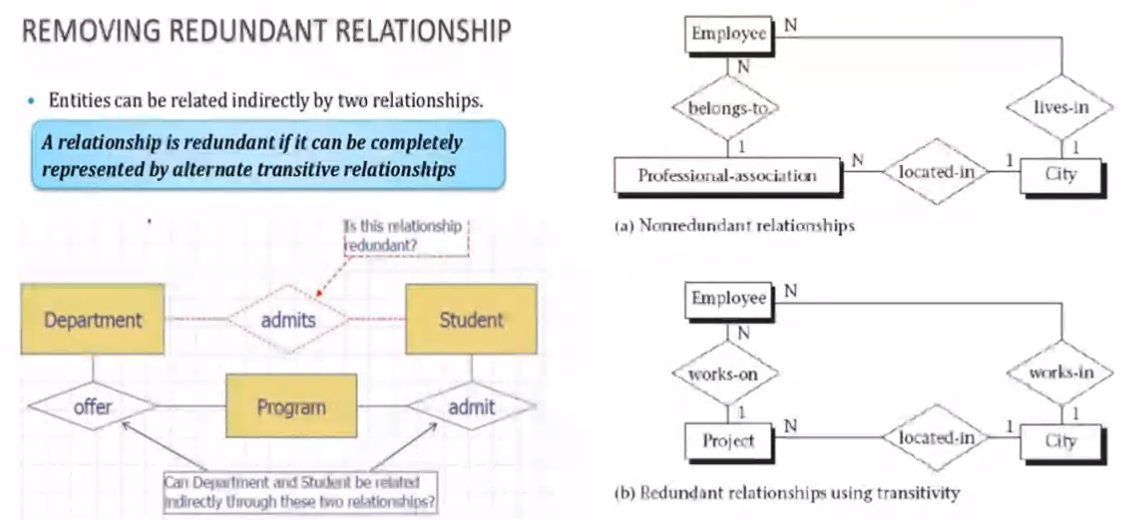
Removing redundant relationship#
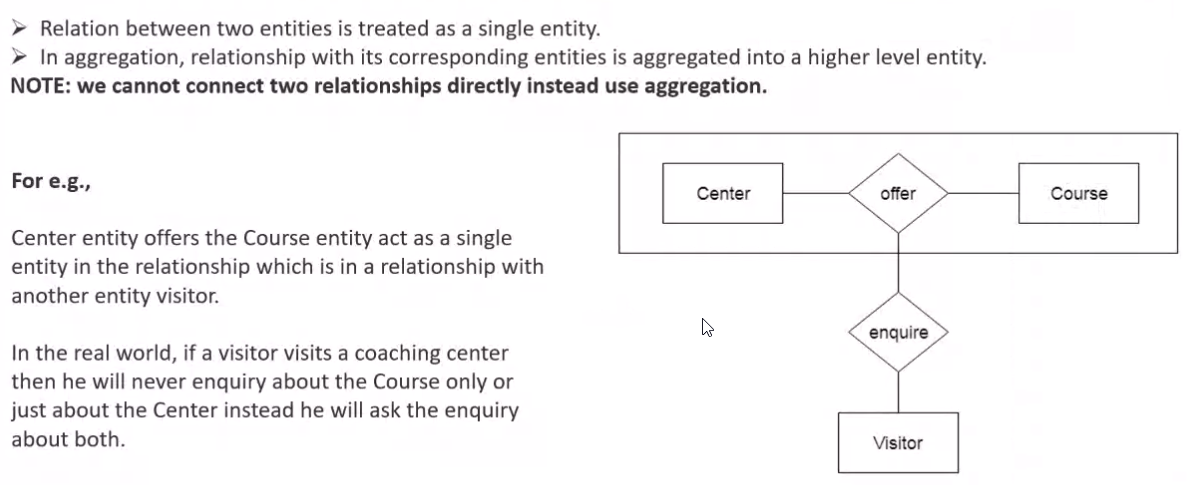
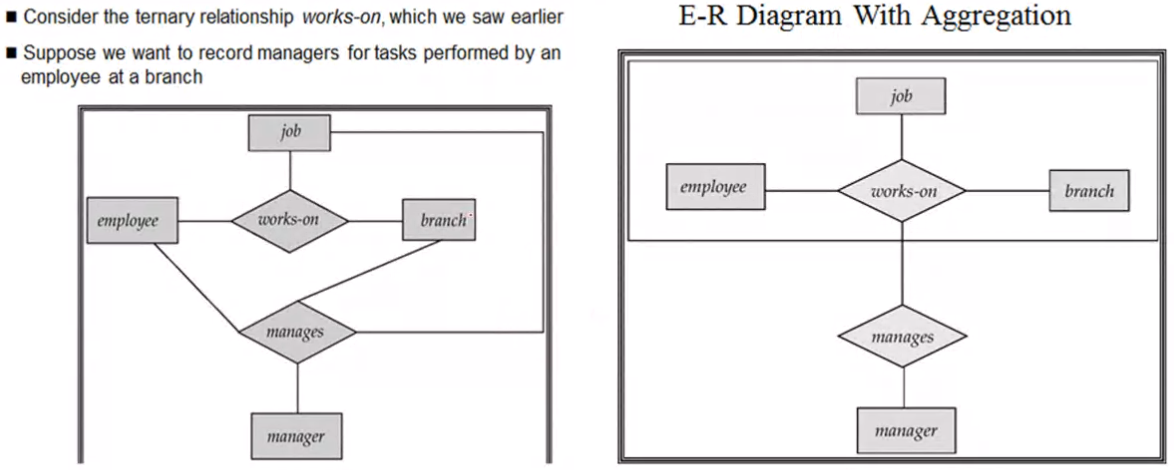
Aggregation#
Questions Answered#
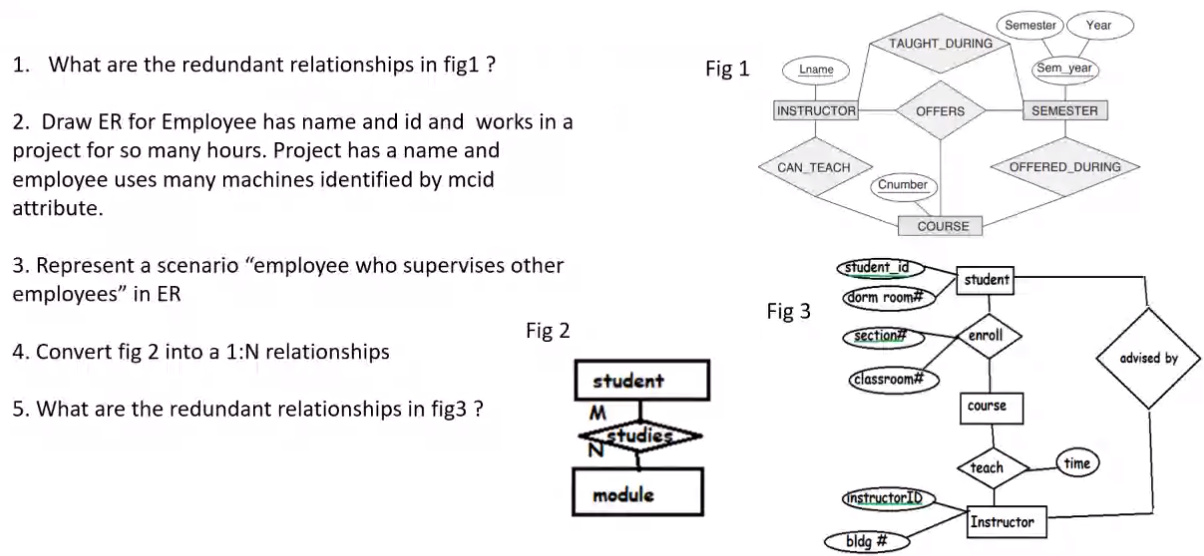
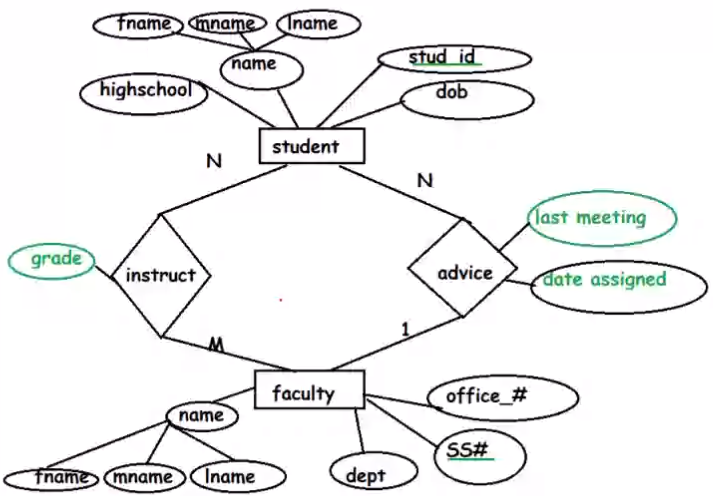
Q1 Answer
Taught during
Q2
Q5
