Module 1#
Terminologies#
Model#
Modeling Language#
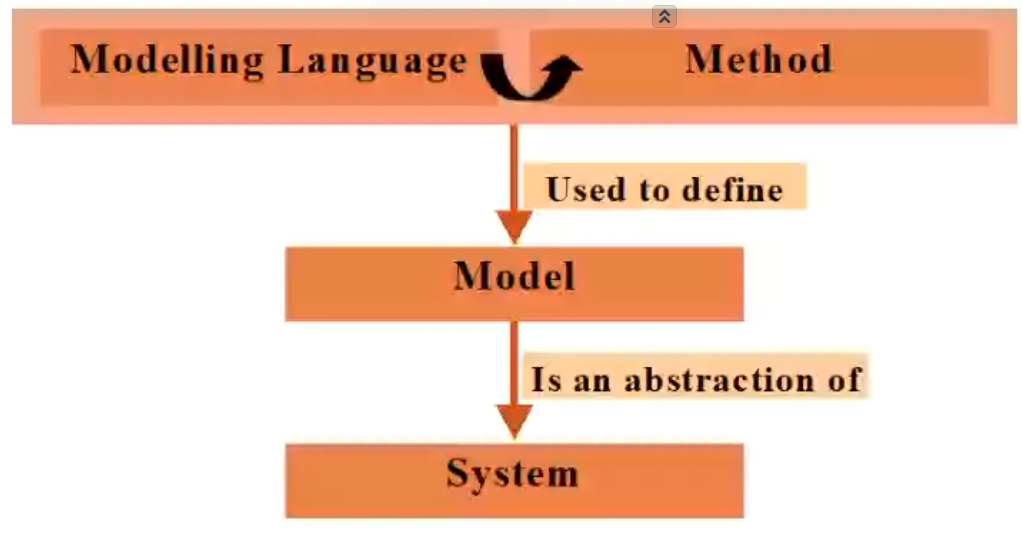
A system is a collection of subsystems organized by models which are inturn depicted by views.
An Example#
System: Aircraft
Models: Flight Simulator, Scale Model
Views: All blueprints, electrical wiring, fuel system
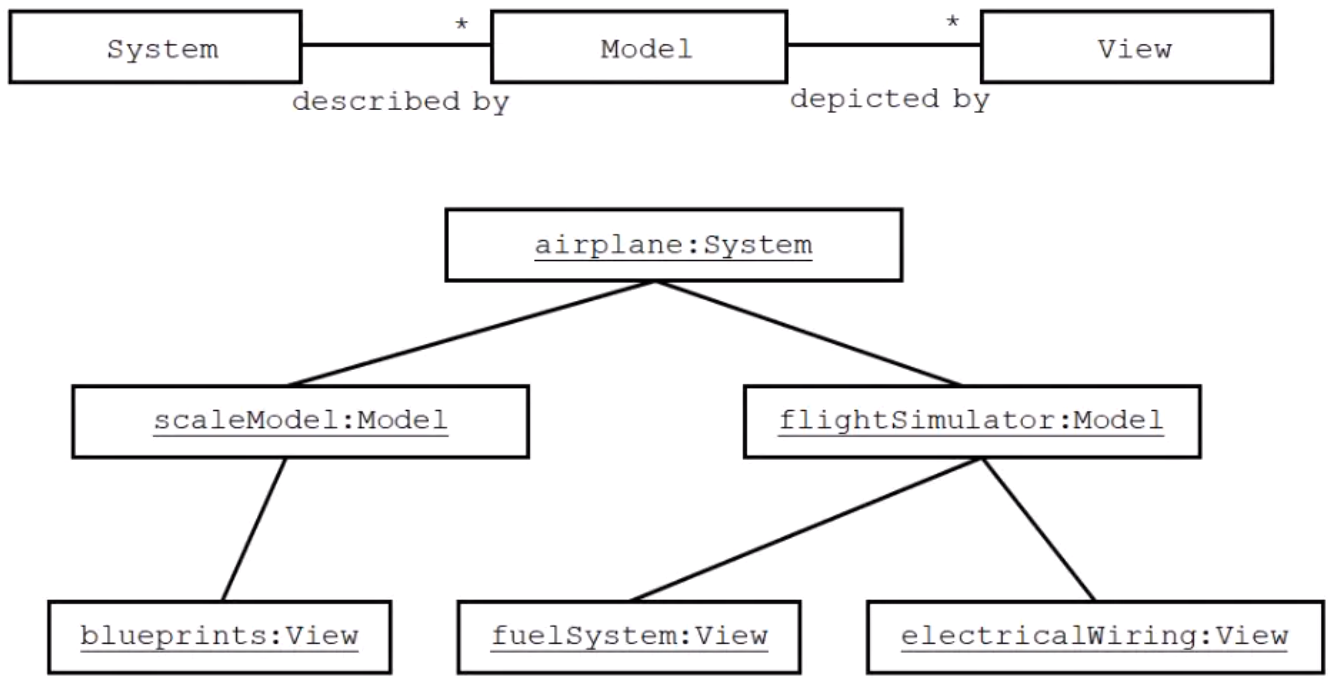
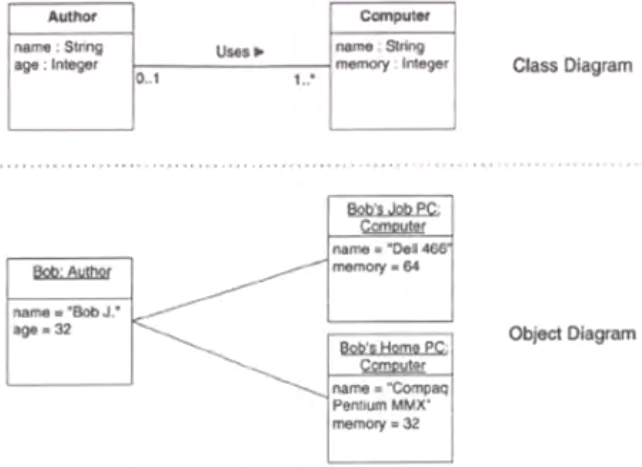
The ':' used to differentiate the name and the type of the object
Object Oriented Modeling#
Why Models?#
- To abstract reality and show essential details and filter out the rest.
- To deal with complexity.
- To allow us to focus on the big picture.
- To understand requirements, design cleanly, more maintainable systems.
Why Objects?#
- To more accurately reflect reality
- Reduce the semantic gap
- To localize changes
Analysis Mode - models related to an investigation of the domain and problem space (Example is a use case model)
Design Mode - models related to the solution (Example is a class diagram)
Elements of modeling language#
- UML is strictly just notations
- UML is not a methodology
- UML is not a process
- UML is not proprietary
- It is a collection of diagrams for system visualization of
- Software architecture
- Behavior
- Physical system
Views in UML#
- Use-case View: A view showing the functionality of the system as perceived by the external actors
- Logical View: A view showing the static structure and dynamic view
- Component View: A view showing the organization of the system
- Concurrency View
- Deployment View
Intro to UML#
Model ELements#
- Class
- Object
- State
- Use Case
UML Diagrams#
- Structural Diagrams
- Behavioral Diagrams
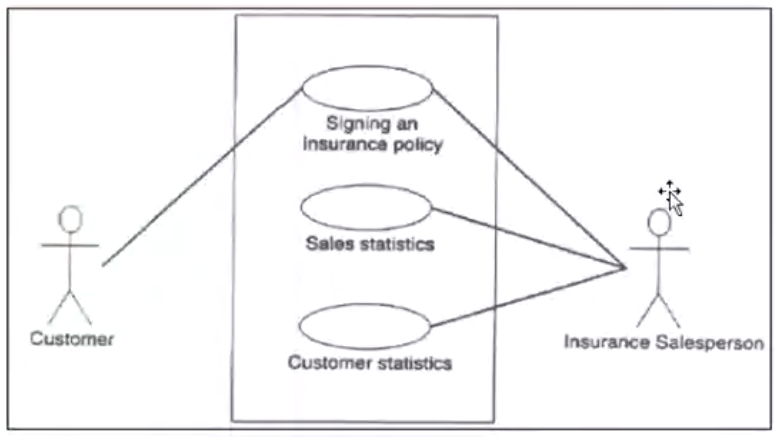
- Use case diagram: External interaction with actors
-
 #
# - Class/Object Diagram: Captures static structural aspects, objects and relationships
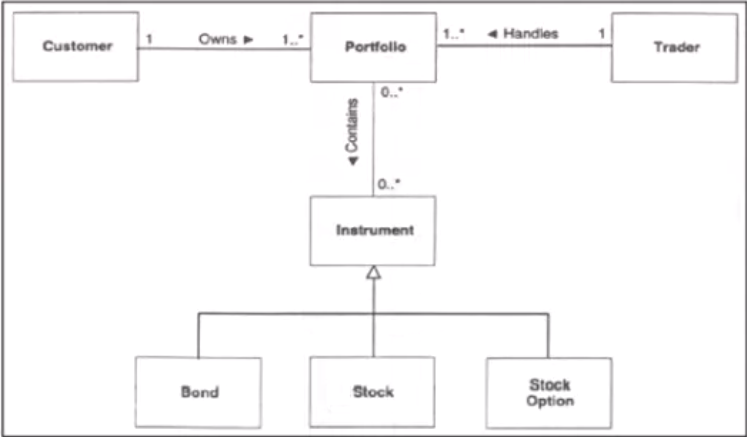
- Class vs Object Diagram:
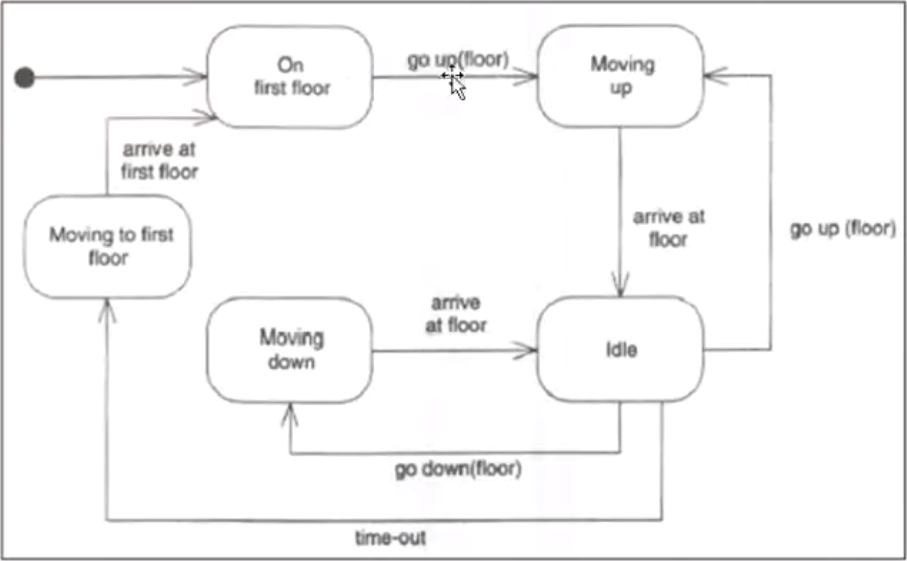
- State Diagram:
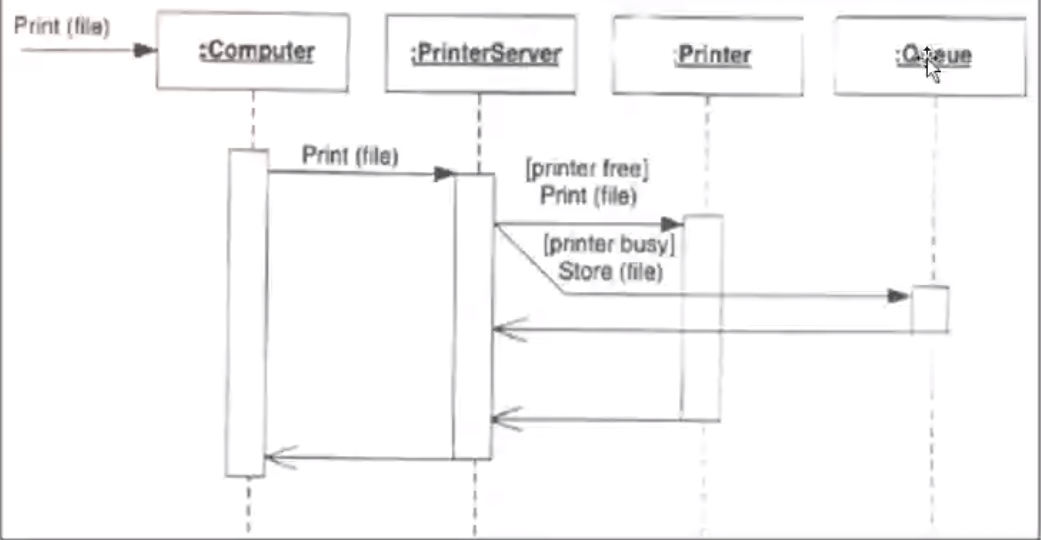
- Sequence Diagram:
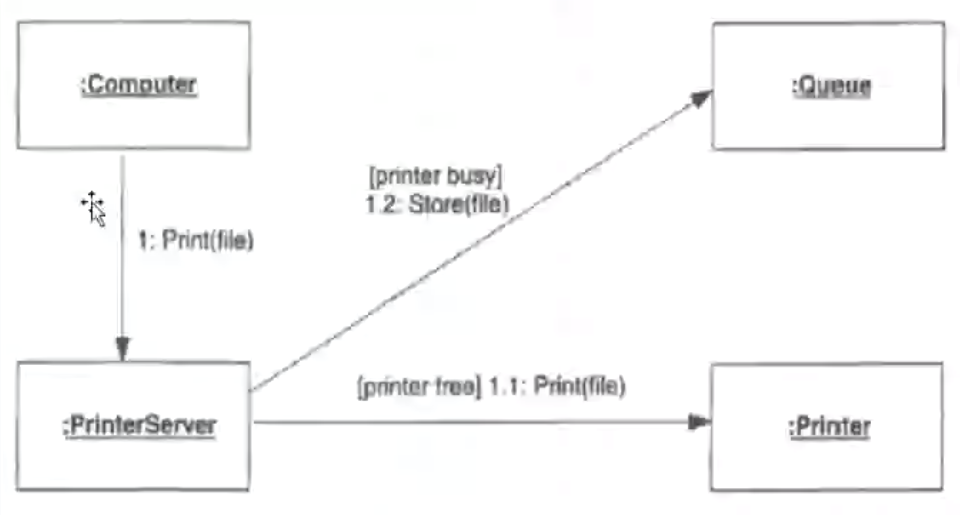
- Collaboration Diagram:
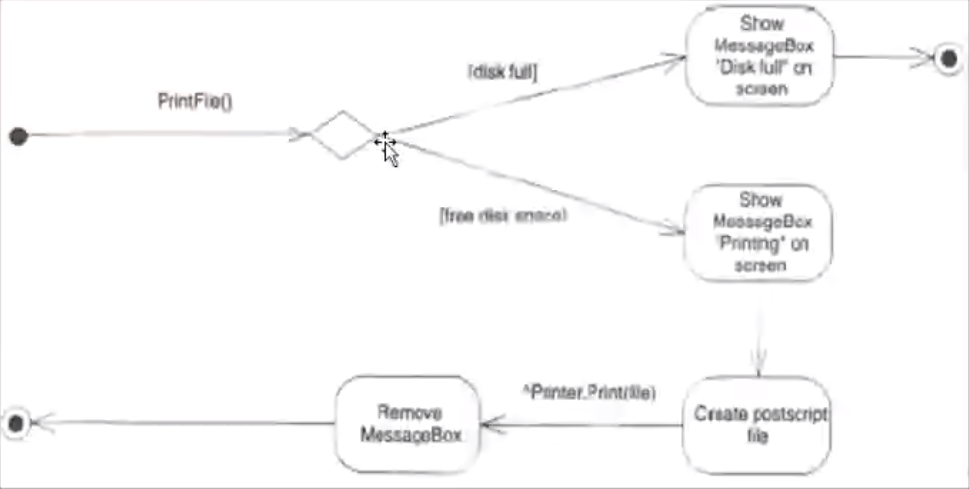
- Activity Diagrams:
- Deployment Diagrams
A process for Making Models#
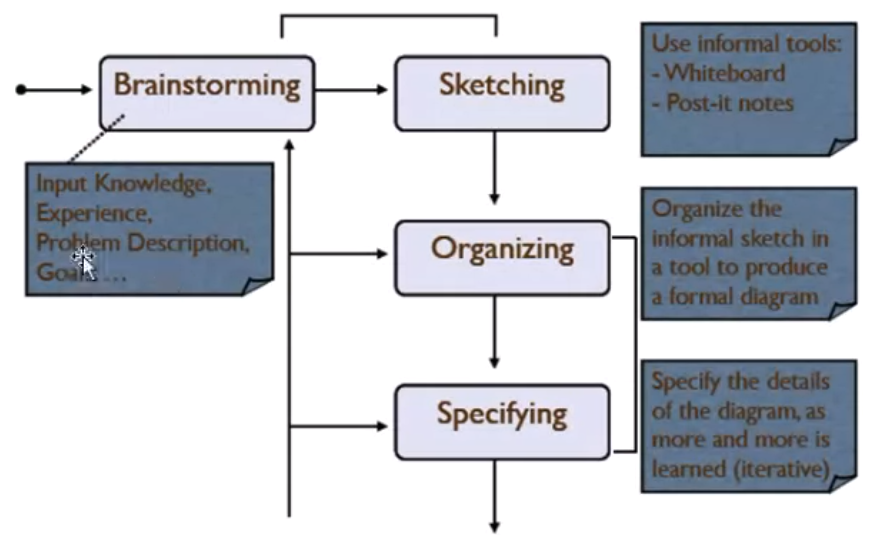
Iterative Development and the Unified Process#
Unified Process#
- The critical idea is iterative development
- Iterative development is successively enlarging and refining a system through multiple iterations, using feedback and adaptation
- Each iteration will include requirements, analysis, design
- The requirements of a project are completely frozen before the design and development process commences. As this approach is not always feasible, there is also a need for flexible and adaptable agile methods that allow late changes in specifications
- RUP is a complete software development process framework developed by Rational Corporation
- It is an iterative development methodolofy based upon six industry proven best practices
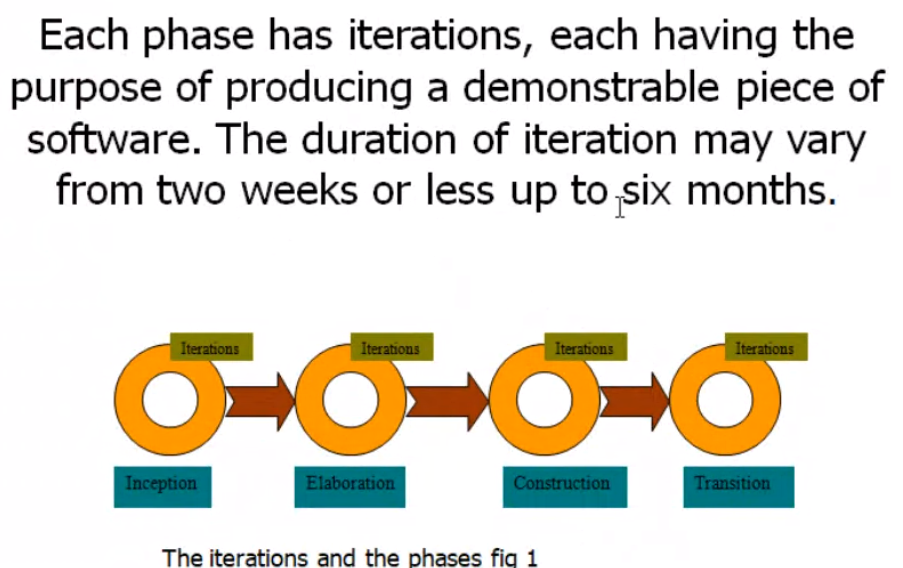
Phases in RUP#
- Inception
- Elaboration
- Construction
- Transition
Iterations#
Resource Histogram#
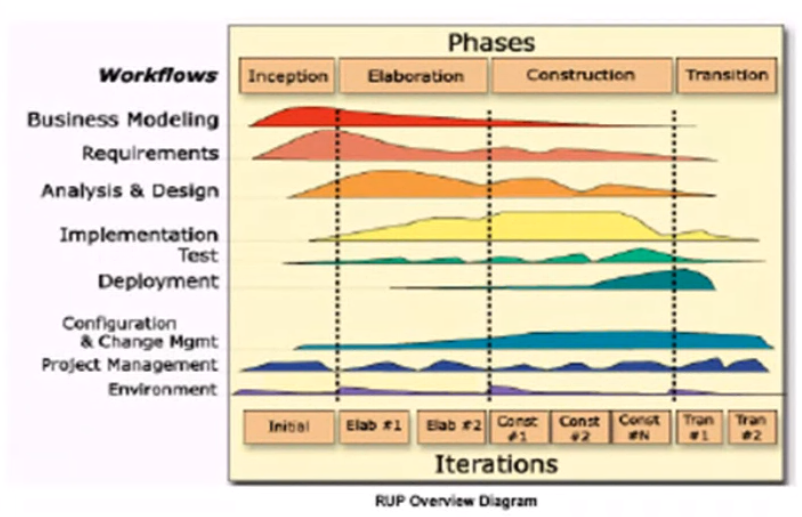
Unified Process Best Practices#

Inception#
- Formulate the scope of the project
- Plan and prepare the use case
- Synthasize candidate architecture
- Prepare the environment
Inception Exit Criteria#

Elaboration#
An analysis is done to determine the risk, stability of ision of what the product is going to become
- Products and artifacts described in the exit criteria of the previous phase
- The plan apporved by the project Management
Elaboration Exit Criteria#

Construction#

Construction Exit Criteria#

Transition#

- Test product in customer side
- Fine tune the product based on customer
- Deliver the product to customer
Transition Exit Criteria#

Advantages of RUP#

Fully Dressed Format

Tags: !OOADIndex