Week 5#
Lecturer: Uma Maheswari, Faculty for BITS Pilani WILP
Date: 21/Aug/2021
Topics Covered#
- Data Model and Schema
- Relational Model (Logical Data Model)
- Characteristics and concepts of relational model
- Relational Schema Diagram Example
Data Model and Schema#
data model captures what kind of data is stored how it must be organized etc
Data model has a description of datam data semantics and consistency constraints of data
There are 3 different types of data models: conceptual data models, logical data models, and physical data models and each has it's own purpose:
1. Conceptual: ER, EER and UML diagrams used to represent how data is organized. We define scope and business concepts and rules
2. Logical: How the system is implemented independent of the DBMS. Will be used by data architects and analysts. The purpose ius to develop technical map of rules and data structures (Schema, it is a plan on how the database needs to be implemented)
3. Physical: This describes how the system will be implemented using a specific DBMS system. This model is typically created by DBA and developers. The files that are used to save tables are part of this model
Relational Model (Logical Data Model)#
- It is based upon the mathematical concepts of relations, set theory and predicate logic
- A relation is a set of values.
- Domain:
- Domain D is a set of atomic values
- By atomic we mean that each value in the domain is indivisible
- Method of specifying a domain is to specify a data type
- USA_Phone_number: The set of ten digit phone numbers valid in US
- SSN: Set of valid nine digit SSNs
- Sex: a member of the set {female, male}
- GPA: A real number between 0.0 to 4.0
- Names: The set of character strings that represent names of person
- The above rules are called logical definitions if domains
- A domain is thus given a name, data type and a format.
- Attribute:
- Attributes are columns for a given entity type and have a name
- The domain for an attribute \(A\) is given as \(dom(A)\) and it holds all the values that the attribute can hold
- Tuple:
- A Row in an entity is called a tuple
- The mapping of attributes and its values
- Example {Name -> "Akhil Sudhakaran", Sex -> Male, IQ -> 9000}
-
Relational Schema:
- Relational schema is given by \(R\), and it is the relation's name. It is denoted by \(R(A_1, A_2, A_3,...,A_n)\)
- Each attribute \(A_i\) is identified by \(dom(A_i)\)
- The degree of a relation is the number of attributes of its relation
- Using data type of each attributem the definition is sometimes written as:
\[STUDENT(Name: string,\ Ssn: string,\ Home\_phone: string,\ Address: string,\ Office\_phone: string,\ Age: integer,\ Gpa: real)\]- Attribute \(A_i\) can be qualified with the relation name \(R\) to which it belongs by using the dot notation \(R.A_i\), for example \(STUDENT.name\)
- Relation State:
- Denoted by \(r(R)\), is a set if n-tuples \(r = \{t_1, t_2, t_3, ... , t_n\}\)
- Each tuple \(t\) is an ordered list of n values \(t=<v_1, v_2, ... , v_n>\)
- Each \(v_i\) is an element of \(dom(A_i)\)
- It is possible for several attributes to have the same domain. The domain 'USA_phone_numbers' can be used for the attributes 'Home_phone' and 'Office_phone' as well
- Relation:
- A named set of tuples all of the same form (Having same set of attributes). The term table is a loose synonym
- A relation state is a subset of the Cartesian product of the domains defining the relation schema
- Relational Database:
- A collection if relations, each one needs to have a logical relationship, then that collection is called relational database
Characteristics and concepts of relational model#
- A relation is a set of tuples and have no duplicates and have no order
- Ordering of tuples cannot be possible
- Logically the tuples have no order
- Physically in disk there can be an order
- When we display a relation as a table, the rows are displated in a vertain ordeer by different attributes
- Ordering if attributes: A tuple is best viewed as a mapping from its attributes.
- The null value: Used for dont know, not applicable or value undefined etc.
- For example if an attribute Phone_number is not available then we can store the value NULL to denote that
- Composite and multivalued attributes are not allowed
- Values of attributes: All values must be atomic and must not contain composite or multi valued.
- r(R) < dom(A_1) x dom(A_2) x ... x dom(A_n)
- R: Schema of relation
- r of R: a specific value or popuilation if R
-
R is also calledf the intension of relation
- Let S_1 = {0, 1}
- Let S_2 - {a, b, c}
- Let R < S1 x S2
- then for example: r(R) = {<0, a>, <0, b>, <1, c>}.
-
There are a lot of constraints or restrictions on the actual valuies in a datrabase state
- Constraints on DBB can generally be divided:
- Implicit constraints: constraints in the data model.No two tupples can have duplicate values
- The salary of employee cannot exceed the salary of the supervisor
- Maximum number of hours an employee can work in a week is 56
- Triggers and assertions can be used to enforce semantic based constraints
-
schema based:
- Constraints expressed in schema, typically done in DDL
- Domain Constraints: Within each tuple, the value of each attribute \(A\) must be atomic. Each attribute must be either null or must be from the \(dom(A)\) Some DBMS allow to impost a not null constraint as well
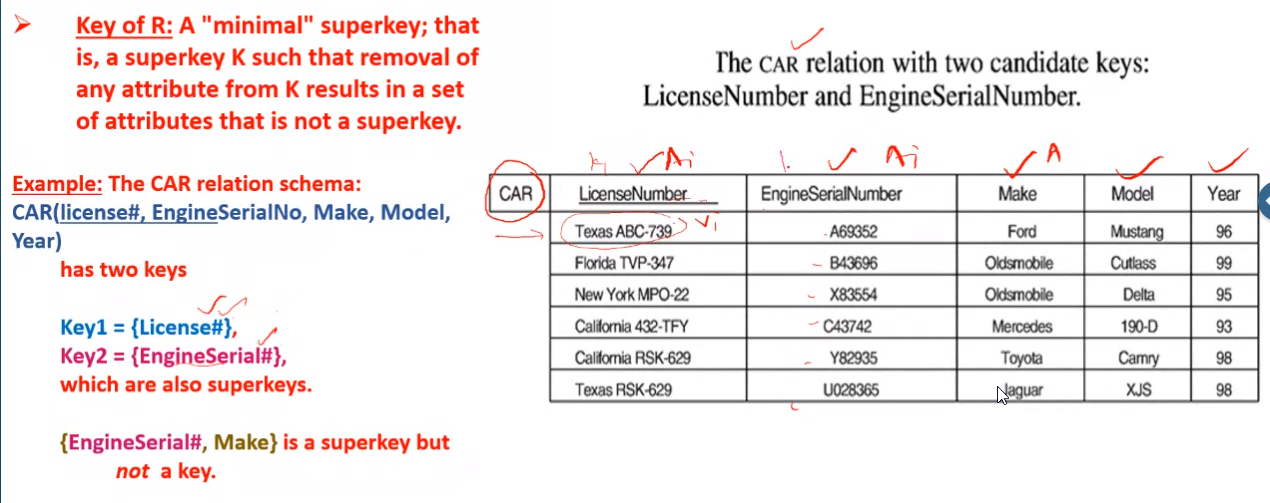
- Key constraint:
- Means no two tuples can have the same combination if values for all their attributes
- Subsets of attributes of a relation in schema \(R\) with the property that no two tuples in any relation state r of R is called a super key.
- Whenever a super key has redundant values, they are removed and a candidate key is generated.
- One from this candidate key is the primary key. These keys are underlined in the relational schema
- Relation database state \(S\) is a set of relational schema \(S = \{R_1, R_2, ... , R_m\}\)
- A snapshot of the relationship database is the data at the current relation schema
- Integrity constraint: This states that no primary key value can be NULL
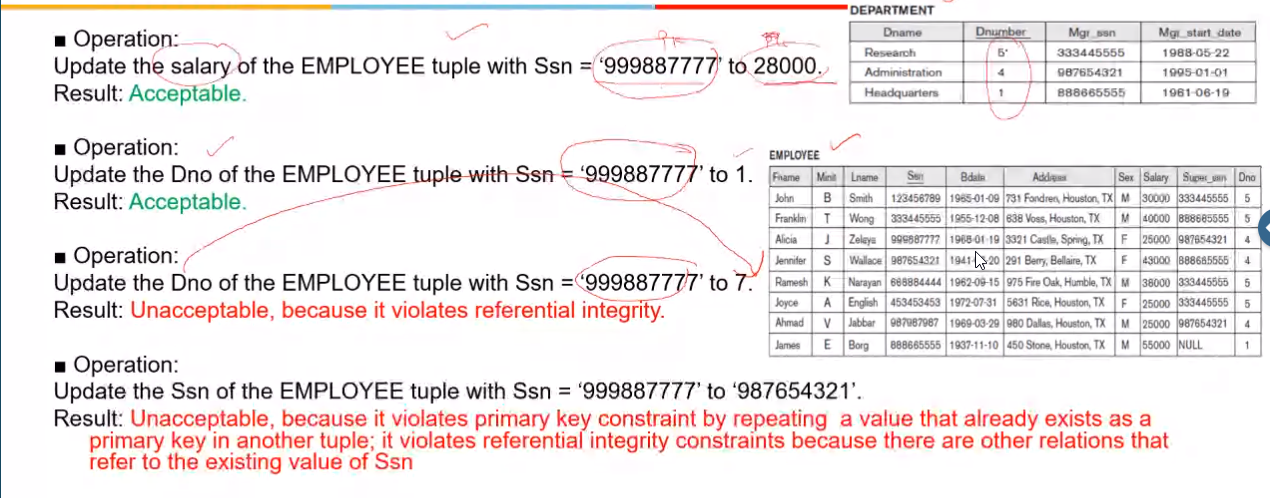
- Referential Integrity Constraint: This is implemented for foreign keys
- Referential Integrity Violation:
- When foreign key is updated and that foreign key is not a PK of the foreign tuple
- When primary key is updated and the entities that refer to this PK as FK must also be updated
-
application based
Relational Schema Diagram Example#

